Involvement of Pin1 induction in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells
- PMID: 19681904
- PMCID: PMC11159919
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01260.x
Involvement of Pin1 induction in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells
Abstract
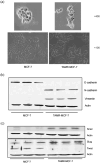
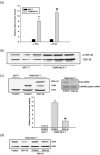
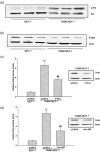
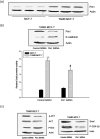
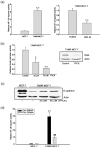
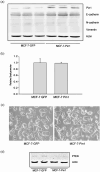
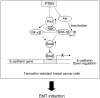
Acquisition of resistance to tamoxifen is a critical therapeutic problem in breast cancer patients. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), where cells undergo a developmental switch from a polarized epithelial phenotype to a highly motile mesenchymal phenotype, is associated with invasion and motility of cancer cells. Here, we found that tamoxifen-resistant (TAMR)-MCF-7 cells had undergone EMT, as evidenced by mesenchymal-like cell shape, downregulation of basal E-cadherin expression, and overexpression of N-cadherin and vimentin, as well as increased Snail transcriptional activity and protein expression. Given the roles of glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3beta and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB in Snail-mediated E-cadherin deregulation during EMT, we examined the role of these signaling pathways in the EMT of TAMR-MCF-7 cells. Both Ser9-phosphorylated GSK-3beta (inactive form) and NF-kappaB reporter activity were increased in TAMR-MCF-7 cells, as was activation of the phosphatase and tensin homolog depleted on chromosome ten (PTEN)-phosphoinositide 3 (PI3)-kinase-Akt pathway. Pin1, a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, was overexpressed in TAMR-MCF-7 cells, and Snail transcription and the expression of EMT markers could be decreased by Pin1 siRNA treatment. These results imply that Pin1 overexpression in TAMR-MCF-7 cells is involved in the EMT process via PTEN-PI3-kinase-Akt-GSK-3beta and/or GSK-3beta-NF-kappaB-dependent Snail activation, and suggest the potential involvement of Pin1 in EMT during breast cancer development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PI3-kinase/p38 kinase-dependent E2F1 activation is critical for Pin1 induction in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells.Mol Cells. 2011 Jul;32(1):107-11. doi: 10.1007/s10059-011-0074-y. Epub 2011 May 11. Mol Cells. 2011. PMID: 21573702 Free PMC article.
-
ERalpha signaling through slug regulates E-cadherin and EMT.Oncogene. 2010 Mar 11;29(10):1451-62. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.433. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20101232
-
Enhancement of vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells: role of Pin1 overexpression.Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Aug;8(8):2163-71. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-1061. Epub 2009 Aug 11. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. PMID: 19671742
-
Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in cell fate and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions.Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;185(1-3):73-84. doi: 10.1159/000101306. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007. PMID: 17587811 Review.
-
The novel role of Yin Yang 1 in the regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer via the dysregulated NF-κB/Snail/YY1/RKIP/PTEN Circuitry.Crit Rev Oncog. 2011;16(3-4):211-26. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.v16.i3-4.50. Crit Rev Oncog. 2011. PMID: 22248055 Review.
Cited by
-
Oncogenic Hijacking of the PIN1 Signaling Network.Front Oncol. 2019 Feb 25;9:94. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00094. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30873382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Programs and Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes: Mediators of Breast Cancer Therapy Resistance.Mol Cancer Res. 2020 Sep;18(9):1257-1270. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0067. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Mol Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32503922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3-kinase/p38 kinase-dependent E2F1 activation is critical for Pin1 induction in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells.Mol Cells. 2011 Jul;32(1):107-11. doi: 10.1007/s10059-011-0074-y. Epub 2011 May 11. Mol Cells. 2011. PMID: 21573702 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between ER and NFκB in resistance to endocrine therapy.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Aug 31;14(4):212. doi: 10.1186/bcr3196. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22963717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional role of miR-10b in tamoxifen resistance of ER-positive breast cancer cells through down-regulation of HDAC4.BMC Cancer. 2015 Jul 24;15:540. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1561-x. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26206152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mueller SO, Clark JA, Mvers PH, Korach KS. Mammary gland development in adult mice requires epithelial and stromal estrogen receptor alpha. Endocrinol 2002; 143: 2357–65. - PubMed
-
- Petrangeli E, Lubrano C, Ortolani F et al . Estrogen receptors: new perspectives in breast cancer management. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1994; 49: 327–31. - PubMed
-
- Rose C, Thorpe SM, Andersen KW et al . Beneficial effect of adjuvant tamoxifen therapy in primary breast cancer patients with high oestrogen receptor values. Lancet 1985; 1: 16–9. - PubMed
-
- Ali S, Coombes RC. Endocrine‐responsive breast cancer cell and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 101–12. - PubMed
-
- Osborne CK, Fuqua SA. Mechanism of tamoxifen resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1994; 32: 49–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

