RNA polymerase III can drive polycistronic expression of functional interfering RNAs designed to resemble microRNAs
- PMID: 19679642
- PMCID: PMC2770651
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp657
RNA polymerase III can drive polycistronic expression of functional interfering RNAs designed to resemble microRNAs
Abstract
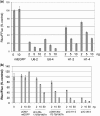
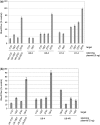
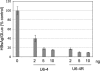
In both research and therapeutic applications of RNA interference, it is often advantageous to silence several targets simultaneously. Toward this end, several groups have developed vectors that utilize the model of endogenously encoded micro (mi) RNAs, where a single RNA polymerase II promoter can drive the expression of multiple interfering RNAs. Stronger pol III promoters have been used to drive individual short hairpin (sh) RNAs, but to date, it has been necessary to repeat the promoter in each silencing cassette to achieve multiplexed expression from a single vector. Here, we show that it is possible to drive polycistronic expression from a single pol III promoter when the interfering RNAs are formatted to resemble miRNAs rather than shRNAs. As many as four miRNAs designed to target hepatitis B virus (HBV) transcripts are shown to be processed and functional in reporter assays as well as in the context of replicating virus in cell culture systems. Although it has been observed that high levels of expression of shRNAs can lead to cytotoxicity, we find no significant evidence in transient transfection assays that the HBV-miRNAs produced by our vectors compete for the activity of endogenously produced miR-122 or for processing of an exogenously expressed miR-EGFP.
Figures
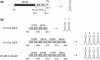
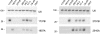
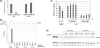
Similar articles
-
Polycistronic expression of interfering RNAs from RNA polymerase III promoters.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;815:347-59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-424-7_26. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22131004
-
Utility of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA promoters for driving the expression of fusion transcripts harboring short hairpin RNAs.Gene Ther. 2008 Feb;15(3):191-202. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3303055. Epub 2007 Nov 1. Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 17972920
-
Vector design for liver-specific expression of multiple interfering RNAs that target hepatitis B virus transcripts.Antiviral Res. 2008 Oct;80(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.04.001. Epub 2008 May 6. Antiviral Res. 2008. PMID: 18499277 Free PMC article.
-
Gene silencing by small regulatory RNAs in mammalian cells.Cell Cycle. 2007 Feb 15;6(4):444-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.4.3807. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17312397 Review.
-
Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jan;8(1):23-36. doi: 10.1038/nrm2085. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17183358 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional regulation of mammalian miRNA genes.Genomics. 2011 Jan;97(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.10.005. Epub 2010 Oct 23. Genomics. 2011. PMID: 20977933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creating a flexible multiple microRNA expression vector by linking precursor microRNAs.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jul 29;411(2):276-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.123. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21726537 Free PMC article.
-
A simplified system for the effective expression and delivery of functional mature microRNAs in mammalian cells.Cancer Gene Ther. 2020 Jun;27(6):424-437. doi: 10.1038/s41417-019-0113-y. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020. PMID: 31222181 Free PMC article.
-
A re-examination of global suppression of RNA interference by HIV-1.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 28;6(2):e17246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017246. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21386885 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-mediated drug resistance in breast cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2011 Aug;2(2):171-185. doi: 10.1007/s13148-011-0040-8. Epub 2011 Jun 27. Clin Epigenetics. 2011. PMID: 21949547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xuan B, Qian Z, Hong J, Huang W. EsiRNAs inhibit hepatitis B virus replication in mice model more efficiently than synthesized siRNAs. Virus. Res. 2006;118:150–155. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe T, Sudoh M, Miyagishi M, Akashi H, Arai M, Inoue K, Taira K, Yoshiba M, Kohara M. Intracellular-diced dsRNA has enhanced efficacy for silencing HCV RNA and overcomes variation in the viral genotype. Gene. Ther. 2006;13:883–892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

