A Legionella type IV effector activates the NF-kappaB pathway by phosphorylating the IkappaB family of inhibitors
- PMID: 19666608
- PMCID: PMC2728961
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0907200106
A Legionella type IV effector activates the NF-kappaB pathway by phosphorylating the IkappaB family of inhibitors
Abstract
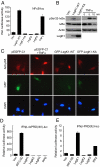
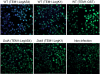
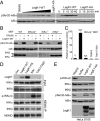
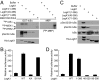
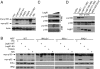
NF-kappaB is critical in innate immune defense responses against invading microbial pathogens. Legionella pneumophila infection of lung macrophages causes Legionnaire's disease with pneumonia symptoms. A set of NF-kappaB-controlled genes involved in inflammation and anti-apoptosis are up-regulated in macrophages upon L. pneumophila infection in a Legionella Dot/Icm type IV secretion system-dependent manner. Among approximately 100 Dot/Icm substrates screened, we identified LegK1 as the sole Legionella protein that harbors a highly potent NF-kappaB-stimulating activity. LegK1 does not affect MAPK and IFN pathways. Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by LegK1 requires its eukaryotic-like Ser/Thr kinase activity and is independent of upstream components in the NF-kappaB pathway, including TRAFs, NIK, MEKK3, and TAK1. Cell-free reconstitution revealed that LegK1 stimulated NF-kappaB activation in the absence of IKKalpha and IKKbeta, and LegK1 efficiently phosphorylated IkappaBalpha on Ser-32 and Ser-36 both in vitro and in cells. LegK1 seems to mimic the host IKK as LegK1 also directly phosphorylated other IkappaB family of inhibitors including p100 in the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway. Phosphorylation of p100 by LegK1 led to its maturation into p52. Thus, LegK1 is a bacterial effector that directly activates the host NF-kappaB signaling and likely plays important roles in modulating macrophage defense or inflammatory responses during L. pneumophila infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
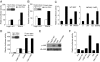
Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of Legionella pneumophila-induced interleukin-8 expression in T cells.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Jan 5;10:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-1. BMC Microbiol. 2010. Retraction in: BMC Microbiol. 2011 Jun 02;11:127. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-127. PMID: 20051107 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Secreted bacterial effectors that inhibit host protein synthesis are critical for induction of the innate immune response to virulent Legionella pneumophila.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Feb;7(2):e1001289. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001289. Epub 2011 Feb 17. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21390206 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella pneumophila-induced PKCalpha-, MAPK-, and NF-kappaB-dependent COX-2 expression in human lung epithelium.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007 Jan;292(1):L267-77. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00100.2006. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17012371
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Manipulation of host vesicular trafficking and innate immune defence by Legionella Dot/Icm effectors.Cell Microbiol. 2011 Dec;13(12):1870-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01710.x. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Cell Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21981078 Review.
Cited by
-
The Dot/Icm effector SdhA is necessary for virulence of Legionella pneumophila in Galleria mellonella and A/J mice.Infect Immun. 2013 Jul;81(7):2598-605. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00296-13. Epub 2013 May 6. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23649096 Free PMC article.
-
Signal Distortion: How Intracellular Pathogens Alter Host Cell Fate by Modulating NF-κB Dynamics.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 14;9:2962. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02962. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30619320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evasion of phagotrophic predation by protist hosts and innate immunity of metazoan hosts by Legionella pneumophila.Cell Microbiol. 2019 Jan;21(1):e12971. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12971. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Cell Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30370624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of NF-κB signalling by microbial pathogens.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Apr;9(4):291-306. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2539. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21383764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effector glycosyltransferases in legionella.Front Microbiol. 2011 Apr 12;2:76. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00076. eCollection 2011. Front Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21833323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Medzhitov R. Recognition of microorganisms and activation of the immune response. Nature. 2007;449:819–826. - PubMed
-
- Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S. Pathogen recognition in the innate immune response. Biochem J. 2009;420:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Perkins ND. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-κB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:49–62. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Bhavsar AP, Guttman JA, Finlay BB. Manipulation of host-cell pathways by bacterial pathogens. Nature. 2007;449:827–834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

