Descending serotonergic facilitation and the antinociceptive effects of pregabalin in a rat model of osteoarthritic pain
- PMID: 19664204
- PMCID: PMC2744671
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-45
Descending serotonergic facilitation and the antinociceptive effects of pregabalin in a rat model of osteoarthritic pain
Abstract
Background: Descending facilitation, from the brainstem, promotes spinal neuronal hyperexcitability and behavioural hypersensitivity in many chronic pain states. We have previously demonstrated enhanced descending facilitation onto dorsal horn neurones in a neuropathic pain model, and shown this to enable the analgesic effectiveness of gabapentin. Here we have tested if this hypothesis applies to other pain states by using a combination of approaches in a rat model of osteoarthritis (OA) to ascertain if 1) a role for descending 5HT mediated facilitation exists, and 2) if pregabalin (a newer analogue of gabapentin) is an effective antinociceptive agent in this model. Further, quantitative-PCR experiments were undertaken to analyse the alpha 2 delta-1 and 5-HT3A subunit mRNA levels in L3-6 DRG in order to assess whether changes in these molecular substrates have a bearing on the pharmacological effects of ondansetron and pregabalin in OA.
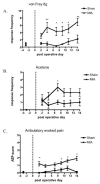
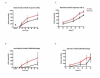
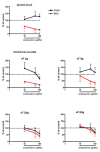
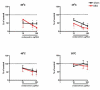
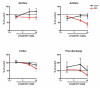
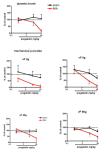
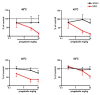
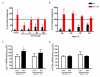
Results: Osteoarthritis was induced via intra-articular injection of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) into the knee joint. Control animals were injected with 0.9% saline. Two weeks later in vivo electrophysiology was performed, comparing the effects of spinal ondansetron (10-100 microg/50 microl) or systemic pregabalin (0.3 - 10 mg/kg) on evoked responses of dorsal horn neurones to electrical, mechanical and thermal stimuli in MIA or control rats. In MIA rats, ondansetron significantly inhibited the evoked responses to both innocuous and noxious natural evoked neuronal responses, whereas only inhibition of noxious evoked responses was seen in controls. Pregabalin significantly inhibited neuronal responses in the MIA rats only; this effect was blocked by a pre-administration of spinal ondansetron. Analysis of alpha 2 delta-1 and 5-HT3A subunit mRNA levels in L3-6 DRG revealed a significant increase in alpha 2 delta-1 levels in ipsilateral L3&4 DRG in MIA rats. 5-HT3A subunit mRNA levels were unchanged.
Conclusion: These data suggest descending serotonergic facilitation plays a role in mediating the brush and innocuous mechanical punctate evoked neuronal responses in MIA rats, suggesting an adaptive change in the excitatory serotonergic drive modulating low threshold evoked neuronal responses in MIA-induced OA pain. This alteration in excitatory serotonergic drive, alongside an increase in alpha 2 delta-1 mRNA levels, may underlie pregabalin's state dependent effects in this model of chronic pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pregabalin suppresses spinal neuronal hyperexcitability and visceral hypersensitivity in the absence of peripheral pathophysiology.Anesthesiology. 2011 Jul;115(1):144-52. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31821f6545. Anesthesiology. 2011. PMID: 21602662 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effects of lacosamide on spinal neuronal and behavioural measures of pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Dec 23;16(6):509. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0509-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25533381 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoarthritis-dependent changes in antinociceptive action of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 sodium channel blockers: An in vivo electrophysiological study in the rat.Neuroscience. 2015 Jun 4;295:103-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.042. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25818052 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic mechanisms of gabapentinoids and effects in experimental pain models: a narrative review.Br J Anaesth. 2018 Jun;120(6):1315-1334. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.02.066. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Br J Anaesth. 2018. PMID: 29793598 Review.
-
The anti-allodynic alpha(2)delta ligand pregabalin inhibits the trafficking of the calcium channel alpha(2)delta-1 subunit to presynaptic terminals in vivo.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Apr;38(2):525-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0380525. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20298215 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrophysiological characterization of activation state-dependent Ca(v)2 channel antagonist TROX-1 in spinal nerve injured rats.Neuroscience. 2015 Jun 25;297:47-57. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.03.057. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25839150 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of combination of meloxicam and pregabalin for pain in knee osteoarthritis.Yonsei Med J. 2013 Sep;54(5):1253-8. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1253. Yonsei Med J. 2013. PMID: 23918578 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Characterisation of peripheral and central components of the rat monoiodoacetate model of Osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 Apr;27(4):712-722. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.12.017. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019. PMID: 30611904 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired chronic pain-like behaviour and altered opioidergic system in the TASTPM mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Eur J Pain. 2019 Jan;23(1):91-106. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1288. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Eur J Pain. 2019. PMID: 29987897 Free PMC article.
-
Recognizing serotonin syndrome in the intensive care unit: a case report of serotonin syndrome in a patient taking amitriptyline, buprenorphine, pregabalin, and fentanyl.AME Case Rep. 2024 Aug 13;8:97. doi: 10.21037/acr-24-40. eCollection 2024. AME Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39380866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO The burden of musculoskeletal conditions at the start of the new millenium. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser WHO. 2003;919:1–218. - PubMed
-
- Creamer P, Hunt M, Dieppe P. Pain mechanisms in osteoarthritis of the knee: effect of intraarticular anesthetic. The Journal of rheumatology. 1996;23:1031–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

