Endotoxin tolerance dysregulates MyD88- and Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-beta-dependent pathways and increases expression of negative regulators of TLR signaling
- PMID: 19656901
- PMCID: PMC2796624
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0309189
Endotoxin tolerance dysregulates MyD88- and Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-beta-dependent pathways and increases expression of negative regulators of TLR signaling
Abstract
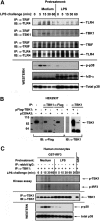
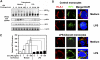
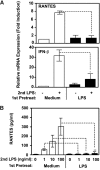
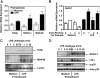
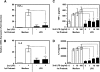
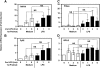
Endotoxin tolerance reprograms cell responses to LPS by repressing expression of proinflammatory cytokines, while not inhibiting production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and antimicrobial effectors. Molecular mechanisms of induction and maintenance of endotoxin tolerance are incompletely understood, particularly with regard to the impact of endotoxin tolerization on signalosome assembly, activation of adaptor-kinase modules, and expression of negative regulators of TLR signaling in human cells. In this study, we examined LPS-mediated activation of MyD88-dependent and Toll-IL-1R-containing adaptor inducing IFN-beta (TRIF)-dependent pathways emanating from TLR4 and expression of negative regulators of TLR signaling in control and endotoxin-tolerant human monocytes. Endotoxin tolerization suppressed LPS-inducible TLR4-TRIF and TRIF-TANK binding kinase (TBK)1 associations, induction of TBK1 kinase activity, activation of IFN regulatory factor (IRF)-3, and expression of RANTES and IFN-beta. Tolerance-mediated dysregulation of the TLR4-TRIF-TBK1 signaling module was accompanied by increased levels of suppressor of IkappaB kinase-epsilon (SIKE) and sterile alpha and Armadillo motif-containing molecule (SARM). LPS-tolerant cells showed increased expression of negative regulators Toll-interacting protein (Tollip), suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-1, IL-1R-associated kinase-M, and SHIP-1, which correlated with reduced p38 phosphorylation, IkappaB-alpha degradation, and inhibited expression of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-8. To examine functional consequences of increased expression of Tollip in LPS-tolerized cells, we overexpressed Tollip in 293/TLR4/MD-2 transfectants and observed blunted LPS-inducible activation of NF-kappaB and RANTES, while TNF-alpha responses were not affected. These data demonstrate dysregulation of TLR4-triggered MyD88- and TRIF-dependent signaling pathways and increased expression of negative regulators of TLR signaling in endotoxin-tolerant human monocytes.
Figures
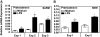
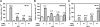
Similar articles
-
Pellino-1 Positively Regulates Toll-like Receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 Signaling and Is Suppressed upon Induction of Endotoxin Tolerance.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 31;290(31):19218-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.640128. Epub 2015 Jun 16. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26082489 Free PMC article.
-
The Asp299Gly polymorphism alters TLR4 signaling by interfering with recruitment of MyD88 and TRIF.J Immunol. 2012 May 1;188(9):4506-15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200202. Epub 2012 Apr 2. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22474023 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS1 regulates the IFN but not NFkappaB pathway in TLR-stimulated human monocytes and macrophages.J Immunol. 2008 Dec 1;181(11):8018-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.11.8018. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19017994 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA in TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance.Cell Mol Immunol. 2011 Sep;8(5):388-403. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2011.26. Epub 2011 Aug 8. Cell Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21822296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TRAM-Related TLR4 Pathway Antagonized by IRAK-M Mediates the Expression of Adhesion/Coactivating Molecules on Low-Grade Inflammatory Monocytes.J Immunol. 2021 Jun 15;206(12):2980-2988. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000978. Epub 2021 May 24. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34031144 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of lipid A pyrophosphorylation and functional lptA reduces inflammation by Neisseria commensals.Infect Immun. 2012 Nov;80(11):4014-26. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00506-12. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22949553 Free PMC article.
-
Tollip or not Tollip: what are the evolving questions behind it?PLoS One. 2014 May 14;9(5):e97219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097219. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24828816 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNAs as regulators of Toll-like receptor signaling and innate immunity.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jun;99(6):839-50. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2RU1215-575R. Epub 2016 Mar 10. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26965636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tollip Deficiency Alters Atherosclerosis and Steatosis by Disrupting Lipophagy.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Apr 10;6(4):e004078. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004078. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28396568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Neill L A. How Toll-like receptors signal: what we know and what we don’t know. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006;18:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway C A., Jr Innate immunity: the virtues of a nonclonal system of recognition. Cell. 1997;91:295–298. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu M Y, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill L A. When signaling pathways collide: positive and negative regulation of toll-like receptor signal transduction. Immunity. 2008;29:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Lien E, Sellati T J, Yoshimura A, Flo T H, Rawadi G, Finberg R W, Carroll J D, Espevik T, Ingalls R R, Radolf J D, Golenbock D T. Toll-like receptor 2 functions as a pattern recognition receptor for diverse bacterial products. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:33419–33425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

