Down-regulation of GRIM-19 expression is associated with hyperactivation of STAT3-induced gene expression and tumor growth in human cervical cancers
- PMID: 19642906
- PMCID: PMC2988461
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2009.0003
Down-regulation of GRIM-19 expression is associated with hyperactivation of STAT3-induced gene expression and tumor growth in human cervical cancers
Abstract
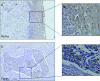
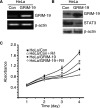
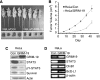
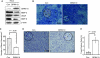
Cervical cancer is the most common malignant disease responsible for the deaths of a large number of women in the developing world. Although certain strains of human papillomavirus (HPV) have been identified as the cause of this disease, events that lead to formation of malignant tumors are not fully clear. STAT3 is a major oncogenic transcription factor involved in the development and progression of a number of human tumors. However, the mechanisms that result in loss of control over STAT3 activity are not understood. Gene associated with Retinoid-Interferon-induced Mortality-19 (GRIM-19) is a tumor-suppressive protein identified using a genetic technique in the interferon/retinoid-induced cell death pathway. Here, we show that reduction in GRIM-19 protein levels occur in a number of primary human cervical cancers. Consequently, these tumors tend to express a high basal level of STAT3 and its downstream target genes. More importantly, using a surrogate model, we show that restoration of GRIM-19 levels reestablishes the control over STAT3-dependent gene expression and tumor growth in vivo. GRIM-19 suppressed the expression of tumor invasion- and angiogenesis-associated factors to limit tumor growth. This study identifies another major novel molecular pathway inactivated during the development of human cervical cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GRIM-19: A master regulator of cytokine induced tumor suppression, metastasis and energy metabolism.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017 Feb;33:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017. PMID: 27659873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene associated with retinoid-interferon-induced mortality-19 suppresses growth of lung adenocarcinoma tumor in vitro and in vivo.Lung Cancer. 2011 Jun;72(3):287-93. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2010.10.001. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Lung Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21040996
-
The effect of a gene associated with retinoid-interferon-induced mortality 19 (GRIM-19) on STAT3-induced gene expression in renal carcinoma.J Biochem. 2018 Oct 1;164(4):285-294. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvy052. J Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29961871
-
Downregulation of GRIM-19 is associated with hyperactivation of p-STAT3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2012 Dec;29(5):3046-54. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0234-8. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22492280
-
GRIM-19 function in cancer development.Mitochondrion. 2011 Sep;11(5):693-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Mitochondrion. 2011. PMID: 21664299 Review.
Cited by
-
A natural food sweetener with anti-pancreatic cancer properties.Oncogenesis. 2016 Apr 11;5(4):e217. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.28. Oncogenesis. 2016. Retraction in: Oncogenesis. 2023 Mar 16;12(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41389-023-00461-7. PMID: 27065453 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
GRIM-19: A master regulator of cytokine induced tumor suppression, metastasis and energy metabolism.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017 Feb;33:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017. PMID: 27659873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional regulatory role of STAT3 in HPV16-mediated cervical carcinogenesis.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 18;8(7):e67849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067849. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874455 Free PMC article.
-
GRIM-19 deficiency promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression and is associated with high TNM stage and Fuhrman grade.Oncol Lett. 2020 Jun;19(6):4115-4121. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11498. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32382350 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-derived mutations in the gene associated with retinoid interferon-induced mortality (GRIM-19) disrupt its anti-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activity and promote oncogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 15;288(11):7930-7941. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.440610. Epub 2013 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23386605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alchanati I. Nallar SC. Sun P. Gao L. Hu J. Stein A. Yakirevich E. Konforty D. Alroy I. Zhao X. Reddy SP. Resnick MB. Kalvakolanu DV. A proteomic analysis reveals the loss of expression of the cell death regulatory gene GRIM-19 in human renal cell carcinomas. Oncogene. 2006;25(54):7138–7147. - PubMed
-
- Braun K. Ehemann V. Waldeck W. Pipkorn R. Corban-Wilhelm H. Jenne J. Gissmann L. Debus J. HPV18 E6 and E7 genes affect cell cycle, pRB and p53 of cervical tumor cells and represent prominent candidates for intervention by use peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) Cancer Lett. 2004;209(1):37–49. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg JF. Wrzeszczynska MH. Devgan G. Zhao Y. Pestell RG. Albanese C. Darnell JE., Jr Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell. 1999;98(3):295–303. - PubMed
-
- Buettner R. Mora LB. Jove R. Activated STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8(4):945–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

