Diverse cross-reactive potential and Vbeta gene usage of an epitope-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte population in monkeys immunized with diverse human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env immunogens
- PMID: 19640988
- PMCID: PMC2748000
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00776-09
Diverse cross-reactive potential and Vbeta gene usage of an epitope-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte population in monkeys immunized with diverse human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env immunogens
Abstract
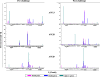
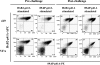
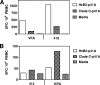
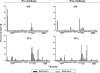
An ideal human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) vaccine would elicit potent cellular and humoral immune responses that recognize diverse strains of the virus. In the present study, combined methodologies (flow cytometry, Vbeta repertoire analysis, and complementarity-determining region 3 sequencing) were used to determine the clonality of CD8(+) T lymphocytes taking part in the recognition of variant epitope peptides elicited in Mamu-A*01-positive rhesus monkeys immunized with vaccines encoding diverse HIV-1 envelopes (Envs). Monkeys immunized with clade B Envs generated CD8(+) T lymphocytes that cross-recognized both clade B- and clade C-p41A epitope peptides using a large degree of diversity in Vbeta gene usage. However, with two monkeys immunized with clade C Env, one monkey exhibited p41A-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL) with the capacity for cross-recognition of variant epitopes, while the other monkey did not. These studies demonstrate that the cross-reactive potential of variant p41A epitope peptide-specific CTL populations can differ between monkeys that share the same restricting major histocompatibility complex class I molecule and receive the same vaccine immunogens.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Use of major histocompatibility complex class I/peptide/beta2M tetramers to quantitate CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for dominant and nondominant viral epitopes in simian-human immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys.J Virol. 1999 Jul;73(7):5466-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.7.5466-5472.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10364294 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant CD8+ T-lymphocyte responses suppress expansion of vaccine-elicited subdominant T lymphocytes in rhesus monkeys challenged with pathogenic simian-human immunodeficiency virus.J Virol. 2009 Oct;83(19):10028-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01015-09. Epub 2009 Jul 29. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19641002 Free PMC article.
-
Definition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 and gp41 cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes and their restricting major histocompatibility complex class I alleles in simian-human immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys.J Virol. 1996 Oct;70(10):7335-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.10.7335-7340.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8794394 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes in protection against equine infectious anemia virus.Anim Health Res Rev. 2004 Dec;5(2):271-6. doi: 10.1079/ahr200482. Anim Health Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 15984338 Review.
-
Identification of highly conserved and broadly cross-reactive HIV type 1 cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes as candidate immunogens for inclusion in Mycobacterium bovis BCG-vectored HIV vaccines.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Sep 20;16(14):1433-43. doi: 10.1089/08892220050140982. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 11018863 Review.
References
-
- Allen, T. M., D. H. O'Connor, P. Jing, J. L. Dzuris, B. R. Mothe, T. U. Vogel, E. Dunphy, M. E. Liebl, C. Emerson, N. Wilson, K. J. Kunstman, X. Wang, D. B. Allison, A. L. Hughes, R. C. Desrosiers, J. D. Altman, S. M. Wolinsky, A. Sette, and D. I. Watkins. 2000. Tat-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes select for SIV escape variants during resolution of primary viraemia. Nature 407:386-390. - PubMed
-
- Appay, V., D. C. Douek, and D. A. Price. 2008. CD8+ T cell efficacy in vaccination and disease. Nat. Med. 14:623-628. - PubMed
-
- Barouch, D. H., A. Craiu, S. Santra, M. A. Egan, J. E. Schmitz, M. J. Kuroda, T. M. Fu, J. H. Nam, L. S. Wyatt, M. A. Lifton, G. R. Krivulka, C. E. Nickerson, C. I. Lord, B. Moss, M. G. Lewis, V. M. Hirsch, J. W. Shiver, and N. L. Letvin. 2001. Elicitation of high-frequency cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses against both dominant and subdominant simian-human immunodeficiency virus epitopes by DNA vaccination of rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 75:2462-2467. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barouch, D. H., J. Powers, D. M. Truitt, M. G. Kishko, J. C. Arthur, F. W. Peyerl, M. J. Kuroda, D. A. Gorgone, M. A. Lifton, C. I. Lord, V. M. Hirsch, D. C. Montefiori, A. Carville, K. G. Mansfield, K. J. Kunstman, S. M. Wolinsky, and N. L. Letvin. 2005. Dynamic immune responses maintain cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope mutations in transmitted simian immunodeficiency virus variants. Nat. Immunol. 6:247-252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

