2B4 (CD244) signaling by recombinant antigen-specific chimeric receptors costimulates natural killer cell activation to leukemia and neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 19638467
- PMCID: PMC2771629
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2810
2B4 (CD244) signaling by recombinant antigen-specific chimeric receptors costimulates natural killer cell activation to leukemia and neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
Purpose: Novel natural killer (NK) cell-directed strategies in cancer immunotherapy aim at specifically modulating the balance between NK cell receptor signals toward tumor-specific activation. The signaling lymphocyte activation molecule-related receptor 2B4 (CD244) is an important regulator of NK cell activation. We investigated whether 2B4-enhanced activation signals can redirect the cytolytic function of human NK cells to NK cell-resistant and autologous leukemia and tumor targets.
Experimental design: In vitro-stimulated NK cells from healthy donors and pediatric leukemia patients were gene modified with CD19 or G(D2)-specific chimeric receptors containing either the T-cell receptor zeta or 2B4 endodomain alone or combined.
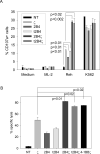
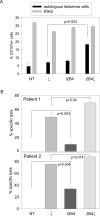
Results: Chimeric 2B4 signaling alone failed to induce interleukin-2 receptor up-regulation and cytokine secretion but triggered a specific degranulation response. Integration of the 2B4 endodomain into T-cell receptor zeta chimeric receptors significantly enhanced all aspects of the NK cell activation response to antigen-expressing leukemia or neuroblastoma cells, including CD25 up-regulation, secretion of IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, release of cytolytic granules, and growth inhibition, and overcame NK cell resistance of autologous leukemia cells while maintaining antigen specificity.
Conclusion: These data indicate that the 2B4 receptor has a potent costimulatory effect in NK cells. Antigen-specific 2B4zeta-expressing NK cells may be a powerful new tool for adoptive immunotherapy of leukemia and other malignancies.
Figures


Comment in
-
Persuading natural killer cells to eliminate bad B cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Aug 1;15(15):4790-1. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0966. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19638468 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
2B4 (CD244) signaling via chimeric receptors costimulates tumor-antigen specific proliferation and in vitro expansion of human T cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009 Dec;58(12):1991-2001. doi: 10.1007/s00262-009-0704-9. Epub 2009 Apr 10. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009. PMID: 19360406 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
2B4 expression on natural killer cells increases in HIV-1 infected patients followed prospectively during highly active antiretroviral therapy.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Sep;141(3):526-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02869.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16045743 Free PMC article.
-
CD19-chimeric antigen receptor-invariant natural killer T cells transactivate NK cells and reduce alloreactivity.Cytotherapy. 2025 Jan;27(1):7-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2024.08.004. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Cytotherapy. 2025. PMID: 39269404
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7(7):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. PMID: 28752910 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetically engineered T cells for cancer immunotherapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019 Sep 20;4:35. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0070-9. eCollection 2019. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019. PMID: 31637014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cells for cancer immunotherapy.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020 Mar;19(3):200-218. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0052-1. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020. PMID: 31907401 Review.
-
NK Cell-Based Immunotherapy and Therapeutic Perspective in Gliomas.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 26;11:751183. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.751183. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34765554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative Strategies of Reprogramming Immune System Cells by Targeting CRISPR/Cas9-Based Genome-Editing Tools: A New Era of Cancer Management.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Sep 29;18:5531-5559. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S424872. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37795042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical development of natural killer cells expressing chimeric antigen receptors.Transfus Apher Sci. 2021 Feb;60(1):103065. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2021.103065. Epub 2021 Jan 10. Transfus Apher Sci. 2021. PMID: 33468407 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burns LJ, Weisdorf DJ, Defor TE, et al. IL-2-based immunotherapy after autologous transplantation for lymphoma and breast cancer induces immune activation and cytokine release: a phase I/II trial. Bone Marrow Transplantation. 2003;32:177–186. - PubMed
-
- Lister J, Rybka WB, Donnenberg AD, et al. Autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation and adoptive immunotherapy with activated natural killer cells in the immediate posttransplant period. Clinical Cancer Research. 1995;1:607–614. - PubMed
-
- Miller JS, Soignier Y, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, et al. Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of human haploidentical NK cells in patients with cancer. Blood. 2005;105:3051–3057. - PubMed
-
- Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, et al. Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science. 2002;295:2097–2100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

