p110 CUX1 homeodomain protein stimulates cell migration and invasion in part through a regulatory cascade culminating in the repression of E-cadherin and occludin
- PMID: 19635798
- PMCID: PMC2785698
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.031849
p110 CUX1 homeodomain protein stimulates cell migration and invasion in part through a regulatory cascade culminating in the repression of E-cadherin and occludin
Abstract
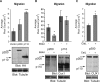
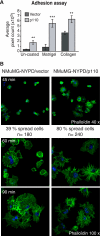
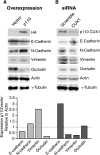
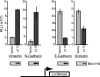
In this study, we investigated the mechanism by which the CUX1 transcription factor can stimulate cell migration and invasion. The full-length p200 CUX1 had a weaker effect than the proteolytically processed p110 isoform; moreover, treatments that affect processing similarly impacted cell migration. We conclude that the stimulatory effect of p200 CUX1 is mediated in part, if not entirely, through the generation of p110 CUX1. We established a list of putative transcriptional targets with functions related to cell motility, and we then identified those targets whose expression was directly regulated by CUX1 in a cell line whose migratory potential was strongly stimulated by CUX1. We identified 18 genes whose expression was directly modulated by p110 CUX1, and its binding to all target promoters was validated in independent chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. These genes code for regulators of Rho-GTPases, cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion proteins, cytoskeleton-associated proteins, and markers of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Interestingly, p110 CUX1 activated the expression of genes that promote cell motility and at the same time repressed genes that inhibit this process. Therefore, the role of p110 CUX1 in cell motility involves its functions in both activation and repression of transcription. This was best exemplified in the regulation of the E-cadherin gene. Indeed, we uncovered a regulatory cascade whereby p110 CUX1 binds to the snail and slug gene promoters, activates their expression, and then cooperates with these transcription factors in the repression of the E-cadherin gene, thereby causing disorganization of cell-cell junctions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The roles of CUX1 homeodomain proteins in the establishment of a transcriptional program required for cell migration and invasion.Cell Adh Migr. 2010 Jul-Sep;4(3):348-52. doi: 10.4161/cam.4.3.11407. Epub 2010 Jul 4. Cell Adh Migr. 2010. PMID: 20224295 Free PMC article.
-
Long-range transcriptional regulation by the p110 CUX1 homeodomain protein on the ENCODE array.BMC Genomics. 2013 Apr 16;14:258. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-258. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23590133 Free PMC article.
-
p110 CUX1 cooperates with E2F transcription factors in the transcriptional activation of cell cycle-regulated genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;28(10):3127-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02089-07. Epub 2008 Mar 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18347061 Free PMC article.
-
CUX1, a haploinsufficient tumour suppressor gene overexpressed in advanced cancers.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Oct;14(10):673-82. doi: 10.1038/nrc3805. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25190083 Review.
-
The multiple roles of CUX1: insights from mouse models and cell-based assays.Gene. 2008 Apr 15;412(1-2):84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.01.017. Epub 2008 Feb 2. Gene. 2008. PMID: 18313863 Review.
Cited by
-
Liquid Biopsy of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived miR-193a-5p in Colorectal Cancer and Discovery of Its Tumor-Suppressor Functions.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 18;10:1372. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01372. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33014778 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated Expression of CUX1 Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Glioma Patients: a Bioinformatic Analysis.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Dec;69(4):527-537. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01355-3. Epub 2019 Aug 3. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31377983
-
The transcription factor CUX1 negatively regulates invasion in castrate resistant prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2020 Mar 3;11(9):846-857. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27494. eCollection 2020 Mar 3. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32180898 Free PMC article.
-
Pterostilbene Changes Epigenetic Marks at Enhancer Regions of Oncogenes in Breast Cancer Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 30;10(8):1232. doi: 10.3390/antiox10081232. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439480 Free PMC article.
-
A fine-tuned β-catenin regulation during proliferation of corneal endothelial cells revealed using proteomics analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 14;10(1):13841. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70800-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32796906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christofori G. (2006) Nature 441, 444–450 - PubMed
-
- Thiery J. P. (2002) Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 442–454 - PubMed
-
- Grünert S., Jechlinger M., Beug H. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 657–665 - PubMed
-
- Peinado H., Olmeda D., Cano A. (2007) Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 415–428 - PubMed
-
- Batlle E., Sancho E., Francí C., Domínguez D., Monfar M., Baulida J., García De Herreros A. (2000) Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 84–89 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

