Metalloproteinase-mediated, context-dependent function of amphiregulin and HB-EGF in human keratinocytes and skin
- PMID: 19609315
- PMCID: PMC2795126
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2009.211
Metalloproteinase-mediated, context-dependent function of amphiregulin and HB-EGF in human keratinocytes and skin
Abstract
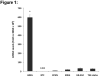
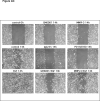
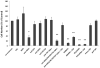
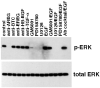
Human keratinocytes (KCs) express multiple EGF receptor (EGFR) ligands; however, their functions in specific cellular contexts remain largely undefined. To address this issue, first we measured mRNA and protein levels for multiple EGFR ligands in KCs and skin. Amphiregulin (AREG) was by far the most abundant EGFR ligand in cultured KCs, with >19 times more mRNA and >7.5 times more shed protein than any other family member. EGFR ligand expression in normal skin was low (<8 per thousand of RPLP0/36B4); however, HB-EGF and AREG mRNAs were strongly induced in human skin organ culture. KC migration in scratch wound assays was highly metalloproteinase (MP)- and EGFR dependent, and was markedly inhibited by EGFR ligand antibodies. However, lentivirus-mediated expression of soluble HB-EGF, but not soluble AREG, strongly enhanced KC migration, even in the presence of MP inhibitors. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-induced ERK phosphorylation was also strongly EGFR and MP dependent and markedly inhibited by neutralization of HB-EGF. In contrast, autocrine KC proliferation and ERK phosphorylation were selectively blocked by neutralization of AREG. These data show that distinct EGFR ligands stimulate KC behavior in different cellular contexts, and in an MP-dependent fashion.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Amphiregulin carboxy-terminal domain is required for autocrine keratinocyte growth.J Invest Dermatol. 2010 Aug;130(8):2031-40. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.98. Epub 2010 Apr 29. J Invest Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20428186 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation in normal human keratinocytes: metalloproteinase-mediated release of amphiregulin triggers signaling from ErbB1 to ERK.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Sep;15(9):4299-309. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-03-0233. Epub 2004 Jul 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15254267 Free PMC article.
-
Human antigen R-mediated mRNA stabilization is required for ultraviolet B-induced autoinduction of amphiregulin in keratinocytes.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10338-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.417527. Epub 2013 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23430747 Free PMC article.
-
TACE/ADAM17 processing of EGFR ligands indicates a role as a physiological convertase.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 May;995:22-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb03207.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12814936 Review.
-
The ADAM17-amphiregulin-EGFR axis in mammary development and cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;13(2):181-94. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9084-6. Epub 2008 May 10. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18470483 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wound Healing Potential of Low Temperature Plasma in Human Primary Epidermal Keratinocytes.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019 Sep 4;16(6):585-593. doi: 10.1007/s13770-019-00215-w. eCollection 2019 Dec. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019. PMID: 31824821 Free PMC article.
-
Amphiregulin regulates odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells by activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathways.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jul 15;13(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02971-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35841013 Free PMC article.
-
IQGAP1 and IQGAP3 Serve Individually Essential Roles in Normal Epidermal Homeostasis and Tumor Progression.J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Sep;135(9):2258-2265. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.140. Epub 2015 Apr 7. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25848980 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-132 enhances transition from inflammation to proliferation during wound healing.J Clin Invest. 2015 Aug 3;125(8):3008-26. doi: 10.1172/JCI79052. Epub 2015 Jun 29. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 26121747 Free PMC article.
-
The EGF receptor ligand amphiregulin controls cell division via FoxM1.Oncogene. 2016 Apr 21;35(16):2075-86. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.269. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26234682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam R, Drummond DR, Solic N, Holt SJ, Sharma RP, Chamberlin SG, et al. Modulation of the receptor binding affinity of amphiregulin by modification of its carboxyl terminal tail. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1266:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Barnard JA, Graves Deal R, Pittelkow MR, DuBois R, Cook P, Ramsey GW, et al. Auto- and cross-induction within the mammalian epidermal growth factor-related peptide family. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:22817–22822. - PubMed
-
- Bhora FY, Dunkin BJ, Batzri S, Aly HM, Bass BL, Sidawy AN, et al. Effect of growth factors on cell proliferation and epithelialization in human skin. J Surg Res. 1995;59:236–244. - PubMed
-
- Burgess AW, Cho HS, Eigenbrot C, Ferguson KM, Garrett TP, Leahy DJ, et al. An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol Cell. 2003;12:541–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

