Differential gene expression patterns of EBV infected EBNA-3A positive and negative human B lymphocytes
- PMID: 19578441
- PMCID: PMC2700271
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000506
Differential gene expression patterns of EBV infected EBNA-3A positive and negative human B lymphocytes
Abstract
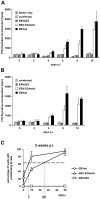
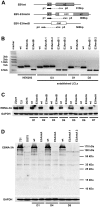
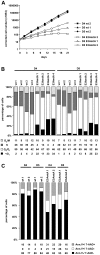
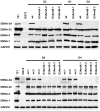
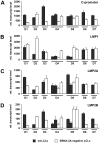
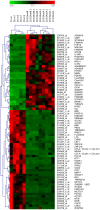
The genome of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encodes 86 proteins, but only a limited set is expressed in EBV-growth transformed B cells, termed lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs). These cells proliferate via the concerted action of EBV nuclear antigens (EBNAs) and latent membrane proteins (LMPs), some of which are rate limiting to establish a stable homeostasis of growth promoting and anti-apoptotic activities. We show here that EBV mutants, which lack the EBNA-3A gene, are impaired but can still initiate cell cycle entry and proliferation of primary human B cells in contrast to an EBNA-2 deficient mutant virus. Surprisingly, and in contrast to previous reports, these viral mutants are attenuated in growth transformation assays but give rise to permanently growing EBNA-3A negative B cell lines which exhibit reduced proliferation rates and elevated levels of apoptosis. Expression profiles of EBNA-3A deficient LCLs are characterized by 129 down-regulated and 167 up-regulated genes, which are significantly enriched for genes involved in apoptotic processes or cell cycle progression like the tumor suppressor gene p16/INK4A, or might contribute to essential steps of the viral life cycle in the infected host. In addition, EBNA-3A cellular target genes remarkably overlap with previously identified targets of EBNA-2. This study comprises the first genome wide expression profiles of EBNA-3A target genes generated within the complex network of viral proteins of the growth transformed B cell and permits a more detailed understanding of EBNA-3A's function and contribution to viral pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
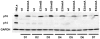
Similar articles
-
EBNA-3B- and EBNA-3C-regulated cellular genes in Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized lymphoblastoid cell lines.J Virol. 2006 Oct;80(20):10139-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00854-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 17005691 Free PMC article.
-
IL-10 can induce the expression of EBV-encoded latent membrane protein-1 (LMP-1) in the absence of EBNA-2 in B lymphocytes and in Burkitt lymphoma- and NK lymphoma-derived cell lines.Blood. 2006 Apr 1;107(7):2928-35. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2569. Epub 2005 Dec 6. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16332968
-
Simultaneous detection of the two main proliferation driving EBV encoded proteins, EBNA-2 and LMP-1 in single B cells.J Immunol Methods. 2012 Nov 30;385(1-2):60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2012.08.008. Epub 2012 Aug 18. J Immunol Methods. 2012. PMID: 22921685
-
EBNA2 and Its Coactivator EBNA-LP.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:35-59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428371 Review.
-
Immortalizing genes of Epstein-Barr virus.Adv Virus Res. 1991;40:19-55. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60276-6. Adv Virus Res. 1991. PMID: 1659776 Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein super-enhancers control B cell growth.Cell Host Microbe. 2015 Feb 11;17(2):205-16. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.12.013. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Cell Host Microbe. 2015. PMID: 25639793 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3C domains necessary for lymphoblastoid cell growth: interaction with RBP-Jkappa regulates TCL1.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(23):12368-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01403-09. Epub 2009 Sep 23. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19776126 Free PMC article.
-
How does Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) complement the activation of Myc in the pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma?Semin Cancer Biol. 2009 Dec;19(6):366-76. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2009.07.007. Epub 2009 Jul 25. Semin Cancer Biol. 2009. PMID: 19635566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First Days in the Life of Naive Human B Lymphocytes Infected with Epstein-Barr Virus.mBio. 2019 Sep 17;10(5):e01723-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01723-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31530670 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive co-operation between the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA3 proteins in the manipulation of host gene expression and epigenetic chromatin modification.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 15;5(11):e13979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013979. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21085583 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

