The phox domain of sorting nexin 5 lacks phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) specificity and preferentially binds to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2)
- PMID: 19553671
- PMCID: PMC2749144
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.008995
The phox domain of sorting nexin 5 lacks phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) specificity and preferentially binds to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2)
Abstract
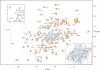
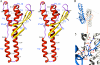
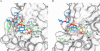
Subcellular retrograde transport of cargo receptors from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network is critically involved in a broad range of physiological and pathological processes and highly regulated by a genetically conserved heteropentameric complex, termed retromer. Among the retromer components identified in mammals, sorting nexin 5 and 1 (SNX5; SNX1) have recently been found to interact, possibly controlling the membrane binding specificity of the complex. To elucidate how the unique sequence features of the SNX5 phox domain (SNX5-PX) influence retrograde transport, we have determined the SNX5-PX structure by NMR and x-ray crystallography at 1.5 A resolution. Although the core fold of SNX5-PX resembles that of other known PX domains, we found novel structural features exclusive to SNX5-PX. It is most noteworthy that in SNX5-PX, a long helical hairpin is added to the core formed by a new alpha2'-helix and a much longer alpha3-helix. This results in a significantly altered overall shape of the protein. In addition, the unique double PXXP motif is tightly packed against the rest of the protein, rendering this part of the structure compact, occluding parts of the putative phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) binding pocket. The PtdIns binding and specificity of SNX5-PX was evaluated by NMR titrations with eight different PtdIns and revealed that SNX5-PX preferentially and specifically binds to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P(2)). The distinct structural and PtdIns binding characteristics of SNX5-PX impart specific properties on SNX5, influencing retromer-mediated regulation of retrograde trafficking of transmembrane cargo receptors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Solution structure of human sorting nexin 22.Protein Sci. 2007 May;16(5):807-14. doi: 10.1110/ps.072752407. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Protein Sci. 2007. PMID: 17400918 Free PMC article.
-
The phox homology (PX) domain-dependent, 3-phosphoinositide-mediated association of sorting nexin-1 with an early sorting endosomal compartment is required for its ability to regulate epidermal growth factor receptor degradation.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 13;277(50):48730-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206986200. Epub 2002 Aug 26. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12198132
-
Inhibitory regulation of EGF receptor degradation by sorting nexin 5.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Apr 7;342(2):537-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.179. Epub 2006 Feb 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16487940
-
Retromer.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Aug;20(4):427-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.03.009. Epub 2008 May 9. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18472259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Phox (PX) domain proteins and membrane traffic.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1761(8):878-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.04.011. Epub 2006 May 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16782399 Review.
Cited by
-
PIP kinases define PI4,5P₂signaling specificity by association with effectors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1851(6):711-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25617736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoform 5 of PIPKIγ regulates the endosomal trafficking and degradation of E-cadherin.J Cell Sci. 2014 May 15;127(Pt 10):2189-203. doi: 10.1242/jcs.132423. Epub 2014 Mar 7. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24610942 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional insights into sorting nexin 5/6 interaction with bacterial effector IncE.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017 Jun 30;2:17030. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2017.30. eCollection 2017. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017. PMID: 29263922 Free PMC article.
-
Structural determinants specific for retromer protein sorting nexin 5 in regulating subcellular retrograde membrane trafficking.J Biomed Res. 2023 Nov 15;37(6):492-506. doi: 10.7555/JBR.37.20230112. J Biomed Res. 2023. PMID: 37964759 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia interfere with an interaction between the mannose-6-phosphate receptor and sorting nexins to counteract host restriction.Elife. 2017 Mar 2;6:e22709. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22709. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28252385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonifacino J. S., Rojas R. (2006) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7,568–579 - PubMed
-
- Vergés M. (2008) Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 271,153–198 - PubMed
-
- Willnow T. E., Petersen C. M., Nykjaer A. (2008) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9,899–909 - PubMed
-
- Ghosh P., Dahms N. M., Kornfeld S. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4,202–212 - PubMed
-
- Eaton S. (2008) Dev. Cell 14,4–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

