TOR complex 2 controls gene silencing, telomere length maintenance, and survival under DNA-damaging conditions
- PMID: 19546237
- PMCID: PMC2725747
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01879-08
TOR complex 2 controls gene silencing, telomere length maintenance, and survival under DNA-damaging conditions
Abstract
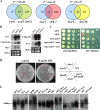
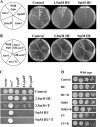
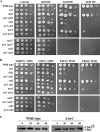
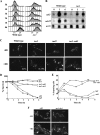
The Target Of Rapamycin (TOR) kinase belongs to the highly conserved eukaryotic family of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-related kinases (PIKKs). TOR proteins are found at the core of two distinct evolutionarily conserved complexes, TORC1 and TORC2. Disruption of TORC1 or TORC2 results in characteristically dissimilar phenotypes. TORC1 is a major cell growth regulator, while the cellular roles of TORC2 are not well understood. In the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Tor1 is a component of the TORC2 complex, which is particularly required during starvation and various stress conditions. Our genome-wide gene expression analysis of Deltator1 mutants indicates an extensive similarity with chromatin structure mutants. Consistently, TORC2 regulates several chromatin-mediated functions, including gene silencing, telomere length maintenance, and tolerance to DNA damage. These novel cellular roles of TORC2 are rapamycin insensitive. Cells lacking Tor1 are highly sensitive to the DNA-damaging drugs hydroxyurea (HU) and methyl methanesulfonate, similar to mutants of the checkpoint kinase Rad3 (ATR). Unlike Rad3, Tor1 is not required for the cell cycle arrest in the presence of damaged DNA. Instead, Tor1 becomes essential for dephosphorylation and reactivation of the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdc2, thus allowing reentry into mitosis following recovery from DNA replication arrest. Taken together, our data highlight critical roles for TORC2 in chromatin metabolism and in promoting mitotic entry, most notably after recovery from DNA-damaging conditions. These data place TOR proteins in line with other PIKK members, such as ATM and ATR, as guardians of genome stability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The reverse, but coordinated, roles of Tor2 (TORC1) and Tor1 (TORC2) kinases for growth, cell cycle and separase-mediated mitosis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Open Biol. 2011 Nov;1(3):110007. doi: 10.1098/rsob.110007. Open Biol. 2011. PMID: 22645648 Free PMC article.
-
TOR complex 2 in fission yeast is required for chromatin-mediated gene silencing and assembly of heterochromatic domains at subtelomeres.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 25;293(21):8138-8150. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002270. Epub 2018 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29632066 Free PMC article.
-
Fission yeast Tor1 functions as part of TORC1 to control mitotic entry through the stress MAPK pathway following nutrient stress.J Cell Sci. 2009 Jun 1;122(Pt 11):1737-46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.049387. Epub 2009 May 5. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19417002
-
TOR signaling in fission yeast.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2008 Jul-Aug;43(4):277-83. doi: 10.1080/10409230802254911. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18756382 Review.
-
TORC1-Dependent Phosphorylation Targets in Fission Yeast.Biomolecules. 2017 Jul 3;7(3):50. doi: 10.3390/biom7030050. Biomolecules. 2017. PMID: 28671615 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The reverse, but coordinated, roles of Tor2 (TORC1) and Tor1 (TORC2) kinases for growth, cell cycle and separase-mediated mitosis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Open Biol. 2011 Nov;1(3):110007. doi: 10.1098/rsob.110007. Open Biol. 2011. PMID: 22645648 Free PMC article.
-
TORC1 Regulates Developmental Responses to Nitrogen Stress via Regulation of the GATA Transcription Factor Gaf1.mBio. 2015 Jul 7;6(4):e00959. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00959-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26152587 Free PMC article.
-
TORC2 mediates the heat stress response in Drosophila by promoting the formation of stress granules.J Cell Sci. 2015 Jul 15;128(14):2497-508. doi: 10.1242/jcs.168724. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26054799 Free PMC article.
-
The Target of Rapamycin Signalling Pathway in Ageing and Lifespan Regulation.Genes (Basel). 2020 Sep 3;11(9):1043. doi: 10.3390/genes11091043. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32899412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A central role for TOR signalling in a yeast model for juvenile CLN3 disease.Microb Cell. 2015 Nov 11;2(12):466-480. doi: 10.15698/mic2015.12.241. Microb Cell. 2015. PMID: 28357272 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
