New insights into the regulation of T cells by gamma(c) family cytokines
- PMID: 19543225
- PMCID: PMC2814538
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2580
New insights into the regulation of T cells by gamma(c) family cytokines
Abstract
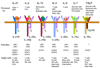
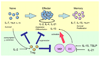
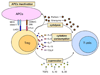
Common cytokine receptor gamma-chain (gamma(c)) family cytokines have crucial roles in the development, proliferation, survival and differentiation of multiple cell lineages of both the innate and adaptive immune systems. In this Review, we focus on our current understanding of the distinct and overlapping effects of interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-7, IL-9, IL-15 and IL-21, as well as the IL-7-related cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), on the survival and proliferation of conventional alphabeta T cells, gammadelta T cells and regulatory T cells. This knowledge potentially allows for the therapeutic manipulation of immune responses for the treatment of cancer, autoimmunity, allergic diseases and immunodeficiency, as well as for vaccine development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patients with T⁺/low NK⁺ IL-2 receptor γ chain deficiency have differentially-impaired cytokine signaling resulting in severe combined immunodeficiency.Eur J Immunol. 2014 Oct;44(10):3129-40. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444689. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25042067
-
Thymic Determinants of γδ T Cell Differentiation.Trends Immunol. 2017 May;38(5):336-344. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Trends Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28285814 Review.
-
T+ NK+ IL-2 Receptor γ Chain Mutation: a Challenging Diagnosis of Atypical Severe Combined Immunodeficiency.J Clin Immunol. 2018 May;38(4):527-536. doi: 10.1007/s10875-018-0514-y. Epub 2018 Jun 9. J Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29948574
-
Interleukin-2 at the crossroads of effector responses, tolerance, and immunotherapy.Immunity. 2013 Jan 24;38(1):13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.01.004. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 23352221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Common Cytokine Receptor γ Chain Family of Cytokines.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 Sep 4;10(9):a028449. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028449. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. PMID: 29038115 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokines of the γ(c) family control CD4+ T cell differentiation and function.Nat Immunol. 2012 Nov;13(11):1037-44. doi: 10.1038/ni.2431. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Nat Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23080204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A profibrotic role for thymic stromal lymphopoietin in systemic sclerosis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 Dec;72(12):2018-23. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202279. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013. PMID: 23413283 Free PMC article.
-
The Thymus in Chagas Disease: Molecular Interactions Involved in Abnormal T-Cell Migration and Differentiation.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 2;11:1838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01838. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antigen-specific IL-2 secretion correlates with NK cell responses after immunization of Tanzanian children with the RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine.J Immunol. 2012 May 15;188(10):5054-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102710. Epub 2012 Apr 13. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22504653 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
STAT5 is a potent negative regulator of TFH cell differentiation.J Exp Med. 2012 Feb 13;209(2):243-50. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111174. Epub 2012 Jan 23. J Exp Med. 2012. PMID: 22271576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leonard WJ. Cytokines and immunodeficiency diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1:200–208. - PubMed
-
- Spolski R, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-21: basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:57–79. - PubMed
-
- Takeshita T, et al. Cloning of the gamma chain of the human IL-2 receptor. Science. 1992;257:379–382. - PubMed
-
-
Wang X, Lupardus P, Laporte SL, Garcia KC. Structural Biology of Shared Cytokine Receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:29–60.
A comprehensive review that details the structures for families of cytokine receptors that contain gp130, γc, or βc, highlights structural similarities and differences, and discusses their abilities to bind ligands and mediate signaling.
-
-
-
Noguchi M, et al. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell. 1993;73:147–157.
This paper demonstrates that mutations in IL2RG results in X-SCID in humans and thus revealed important roles for γc in T and NK cell development. The authors correctly speculated that γc has major roles beyond the action of IL-2.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

