Conformational changes in switch I of EF-G drive its directional cycling on and off the ribosome
- PMID: 19536129
- PMCID: PMC2718289
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.169
Conformational changes in switch I of EF-G drive its directional cycling on and off the ribosome
Abstract
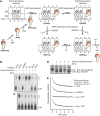
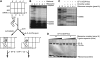
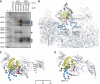
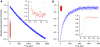
We have trapped elongation factor G (EF-G) from Escherichia coli in six, functionally defined states, representing intermediates in its unidirectional catalytic cycle, which couples GTP hydrolysis to tRNA-mRNA translocation in the ribosome. By probing EF-G with trypsin in each state, we identified a substantial conformational change involving its conserved switch I (sw1) element, which contacts the GTP substrate. By attaching FeBABE (a hydroxyl radical generating probe) to sw1, we could monitor sw1 movement (by approximately 20 A), relative to the 70S ribosome, during the EF-G cycle. In free EF-G, sw1 is disordered, particularly in GDP-bound and nucleotide-free states. On EF-G*GTP binding to the ribosome, sw1 becomes structured and tucked inside the ribosome, thereby locking GTP onto EF-G. After hydrolysis and translocation, sw1 flips out from the ribosome, greatly accelerating release of GDP and EF-G from the ribosome. Collectively, our results support a central role of sw1 in driving the EF-G cycle during protein synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Time-resolved cryo-EM visualizes ribosomal translocation with EF-G and GTP.Nat Commun. 2021 Dec 13;12(1):7236. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27415-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34903725 Free PMC article.
-
Intramolecular movements in EF-G, trapped at different stages in its GTP hydrolytic cycle, probed by FRET.J Mol Biol. 2010 Apr 16;397(5):1245-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.02.039. Epub 2010 Feb 26. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20219471
-
Coordinated conformational and compositional dynamics drive ribosome translocation.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Jun;20(6):718-27. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2567. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23624862 Free PMC article.
-
How can elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu discriminate the functional state of the ribosome using the same binding site?FEBS Lett. 2005 Oct 24;579(25):5439-42. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.09.010. Epub 2005 Sep 26. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 16213500 Review.
-
Translational elongation factor G: a GTP-driven motor of the ribosome.Essays Biochem. 2000;35:117-29. doi: 10.1042/bse0350117. Essays Biochem. 2000. PMID: 12471894 Review.
Cited by
-
Time-resolved cryo-EM visualizes ribosomal translocation with EF-G and GTP.Nat Commun. 2021 Dec 13;12(1):7236. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27415-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34903725 Free PMC article.
-
Head swivel on the ribosome facilitates translocation by means of intra-subunit tRNA hybrid sites.Nature. 2010 Dec 2;468(7324):713-6. doi: 10.1038/nature09547. Nature. 2010. PMID: 21124459 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a fluorescent-mRNA based real-time assay for precise kinetic measurements of ribosomal translocation.RNA Biol. 2021 Dec;18(12):2363-2375. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1913312. Epub 2021 May 3. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33938388 Free PMC article.
-
Correlated conformational events in EF-G and the ribosome regulate translocation.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Dec;17(12):1470-7. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1925. Epub 2010 Nov 7. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 21057527 Free PMC article.
-
Archaeal ribosomal stalk protein interacts with translation factors in a nucleotide-independent manner via its conserved C terminus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 6;109(10):3748-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112934109. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22355137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel K, Yoder MD, Hilgenfeld R, Jurnak F (1996) An alpha to beta conformational switch in EF-Tu. Structure 4: 1153–1159 - PubMed
-
- Baca OG, Rohrbach MS, Bodley JW (1976) Equilibrium measurements of the interactions of guanine nucleotides with Escherichia coli elongation factor G and the ribosome. Biochemistry 15: 4570–4574 - PubMed
-
- Berchtold H, Reshetnikova L, Reiser CO, Schirmer NK, Sprinzl M, Hilgenfeld R (1993) Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature 365: 126–132 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

