X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and its E3 ligase activity promote transforming growth factor-{beta}-mediated nuclear factor-{kappa}B activation during breast cancer progression
- PMID: 19531477
- PMCID: PMC2755844
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.018374
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and its E3 ligase activity promote transforming growth factor-{beta}-mediated nuclear factor-{kappa}B activation during breast cancer progression
Abstract
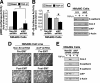
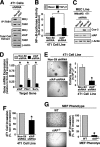
The precise sequence of events that enable mammary tumorigenesis to convert transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter remains incompletely understood. We show here that X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (xIAP) is essential for the ability of TGF-beta to stimulate nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) in metastatic 4T1 breast cancer cells. Indeed whereas TGF-beta suppressed NF-kappaB activity in normal mammary epithelial cells, those engineered to overexpress xIAP demonstrated activation of NF-kappaB when stimulated with TGF-beta. Additionally up-regulated xIAP expression also potentiated the basal and TGF-beta-stimulated transcriptional activities of Smad2/3 and NF-kappaB. Mechanistically xIAP (i) interacted physically with the TGF-beta type I receptor, (ii) mediated the ubiquitination of TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), and (iii) facilitated the formation of complexes between TAK1-binding protein 1 (TAB1) and IkappaB kinase beta that enabled TGF-beta to activate p65/RelA and to induce the expression of prometastatic (i.e. cyclooxygenase-2 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1) and prosurvival (i.e. survivin) genes. We further observed that inhibiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase function of xIAP or expressing a mutant ubiquitin protein (i.e. K63R-ubiquitin) was capable of blocking xIAP- and TGF-beta-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Functionally xIAP deficiency dramatically reduced the coupling of TGF-beta to Smad2/3 in NMuMG cells as well as inhibited their expression of mesenchymal markers in response to TGF-beta. More importantly, xIAP deficiency also abrogated the formation of TAB1.IkappaB kinase beta complexes in 4T1 breast cancer cells, thereby diminishing their activation of NF-kappaB, their expression of prosurvival/metastatic genes, their invasion through synthetic basement membranes, and their growth in soft agar. Collectively our findings have defined a novel role for xIAP in mediating oncogenic signaling by TGF-beta in breast cancer cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Altered TAB1:I kappaB kinase interaction promotes transforming growth factor beta-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB activation during breast cancer progression.Cancer Res. 2008 Mar 1;68(5):1462-70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3094. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18316610 Free PMC article.
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) inhibits c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) activation by transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) through ubiquitin-mediated proteosomal degradation of the TGF-beta1-activated kinase 1 (TAK1).J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 18;280(46):38599-608. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505671200. Epub 2005 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16157589
-
Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in NB-4, an acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line, through up-regulation of p73 via suppression of nuclear factor kappa B-mediated inhibition of p73 transcription and prevention of NF-kappaB-mediated induction of XIAP, cIAP2, BCL-XL and survivin.Med Oncol. 2010 Sep;27(3):833-42. doi: 10.1007/s12032-009-9294-9. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Med Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19763917
-
The role of ubiquitin in NF-kappaB regulatory pathways.Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:769-96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.070907.102750. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19489733 Review.
-
XIAP as a ubiquitin ligase in cellular signaling.Cell Death Differ. 2010 Jan;17(1):54-60. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.81. Cell Death Differ. 2010. PMID: 19590513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A small peptide modeled after the NRAGE repeat domain inhibits XIAP-TAB1-TAK1 signaling for NF-κB activation and apoptosis in P19 cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e20659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020659. Epub 2011 Jul 18. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21789165 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β upregulates miR-181a expression to promote breast cancer metastasis.J Clin Invest. 2013 Jan;123(1):150-63. doi: 10.1172/JCI64946. Epub 2012 Dec 17. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23241956 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
miR-203 inhibits ovarian tumor metastasis by targeting BIRC5 and attenuating the TGFβ pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 21;37(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0906-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30241553 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated WAVE3 expression is essential for TGF-β-mediated EMT and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Nov;142(2):341-53. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2753-1. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 24197660 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Fighting Against Multiple Opponents.Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2017 May 15;10:1179064417709287. doi: 10.1177/1179064417709287. eCollection 2017. Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2017. PMID: 28579826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

