Directed mammalian gene regulatory networks using expression and comparative genomic hybridization microarray data from radiation hybrids
- PMID: 19521529
- PMCID: PMC2690838
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000407
Directed mammalian gene regulatory networks using expression and comparative genomic hybridization microarray data from radiation hybrids
Abstract
Meiotic mapping of quantitative trait loci regulating expression (eQTLs) has allowed the construction of gene networks. However, the limited mapping resolution of these studies has meant that genotype data are largely ignored, leading to undirected networks that fail to capture regulatory hierarchies. Here we use high resolution mapping of copy number eQTLs (ceQTLs) in a mouse-hamster radiation hybrid (RH) panel to construct directed genetic networks in the mammalian cell. The RH network covering 20,145 mouse genes had significant overlap with, and similar topological structures to, existing biological networks. Upregulated edges in the RH network had significantly more overlap than downregulated. This suggests repressive relationships between genes are missed by existing approaches, perhaps because the corresponding proteins are not present in the cell at the same time and therefore unlikely to interact. Gene essentiality was positively correlated with connectivity and betweenness centrality in the RH network, strengthening the centrality-lethality principle in mammals. Consistent with their regulatory role, transcription factors had significantly more outgoing edges (regulating) than incoming (regulated) in the RH network, a feature hidden by conventional undirected networks. Directed RH genetic networks thus showed concordance with pre-existing networks while also yielding information inaccessible to current undirected approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
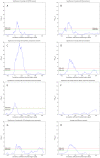
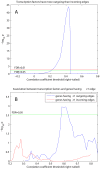
 values over results from A to G. One-sided Fisher's exact and chi-square tests used to assess overlap significance.
values over results from A to G. One-sided Fisher's exact and chi-square tests used to assess overlap significance.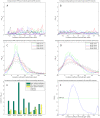
 values for overlap between randomly permuted RH networks and different existing datasets (HPRD, KEGG, SymAtlas coexpression, GO, GO-molecular function, GO-cellular component and GO-biological process annotation networks). (C) Overlap between RH networks constructed from a subset of randomly selected RH clones and HPRD network. Mean of overlap significance (solid line) over 50 random subsets shown with standard errors calculated by bootstrapping (dash-dot line). (D) Same as (C) except averaged
values for overlap between randomly permuted RH networks and different existing datasets (HPRD, KEGG, SymAtlas coexpression, GO, GO-molecular function, GO-cellular component and GO-biological process annotation networks). (C) Overlap between RH networks constructed from a subset of randomly selected RH clones and HPRD network. Mean of overlap significance (solid line) over 50 random subsets shown with standard errors calculated by bootstrapping (dash-dot line). (D) Same as (C) except averaged  values over different existing datasets. (E) Comparing different thresholding approaches. Maximum
values over different existing datasets. (E) Comparing different thresholding approaches. Maximum  over varying correlation coefficient thresholds shown. (F) Comparing betweenness centralities of RH and HPRD networks. P-values of Spearman correlation coefficients (one-sided, positive direction) between the betweenness centralities of RH and HPRD networks shown.
over varying correlation coefficient thresholds shown. (F) Comparing betweenness centralities of RH and HPRD networks. P-values of Spearman correlation coefficients (one-sided, positive direction) between the betweenness centralities of RH and HPRD networks shown.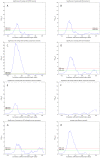
Similar articles
-
Fine mapping of regulatory loci for mammalian gene expression using radiation hybrids.Nat Genet. 2008 Apr;40(4):421-9. doi: 10.1038/ng.113. Epub 2008 Mar 23. Nat Genet. 2008. PMID: 18362883 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of genome-wide copy number variation on expression in mammalian cells.BMC Genomics. 2011 Nov 16;12:562. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-562. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22085887 Free PMC article.
-
Causal inference of regulator-target pairs by gene mapping of expression phenotypes.BMC Genomics. 2006 May 24;7:125. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-125. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16719927 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray-based comparative genomic hybridization (array-CGH) as a useful tool for identifying genes involved in Glioblastoma (GB).Methods Mol Biol. 2010;653:35-45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-759-4_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20721736 Review.
-
Moving toward a system genetics view of disease.Mamm Genome. 2007 Jul;18(6-7):389-401. doi: 10.1007/s00335-007-9040-6. Epub 2007 Jul 26. Mamm Genome. 2007. PMID: 17653589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic screening reveals a link between Wnt signaling and antitubulin drugs.Pharmacogenomics J. 2016 Apr;16(2):164-72. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2015.50. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Pharmacogenomics J. 2016. PMID: 26149735 Free PMC article.
-
SNP microarray analyses reveal copy number alterations and progressive genome reorganization during tumor development in SVT/t driven mice breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2012 Aug 31;12:380. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-380. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22935085 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Effective Mapping of Genetic Interactions in Mammalian Cells.Front Genet. 2021 Aug 5;12:703738. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.703738. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34434222 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide map of human genetic interactions inferred from radiation hybrid genotypes.Genome Res. 2010 Aug;20(8):1122-32. doi: 10.1101/gr.104216.109. Epub 2010 May 27. Genome Res. 2010. PMID: 20508145 Free PMC article.
-
Systems genetics in "-omics" era: current and future development.Theory Biosci. 2013 Mar;132(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s12064-012-0168-x. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Theory Biosci. 2013. PMID: 23138757 Review.
References
-
- Vidal M. A biological atlas of functional maps. Cell. 2001;104:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Ge H, Walhout AJ, Vidal M. Integrating ‘omic’ information: a bridge between genomics and systems biology. Trends Genet. 2003;10:551–560. - PubMed
-
- Stuart JM, Segal E, Koller D, Kim SK. A gene-coexpression network for global discovery of conserved genetic modules. Science. 2003;302:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Cusick ME, Klitgord N, Vidal M, Hill DE. Interactome: gateway into systems biology. Human Molecular Genetics. 2005;14:R171–R181. - PubMed
-
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, et al. Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature. 2005;437:1173–1178. - PubMed

