The role of CYP26 enzymes in retinoic acid clearance
- PMID: 19519282
- PMCID: PMC2730205
- DOI: 10.1517/17425250903032681
The role of CYP26 enzymes in retinoic acid clearance
Abstract
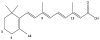
Retinoic acid (RA) is a critical signaling molecule that regulates gene transcription and the cell cycle. Understanding of RA signaling has increased dramatically over the past decades, but the connection between whole body RA homeostasis and gene regulation in individual cells is still unclear. It has been proposed that cytochrome P450 family 26 (CYP26) enzymes have a role in determining the cellular exposure to RA by inactivating RA in cells that do not need RA. The CYP26 enzymes have been shown to metabolize RA efficiently and they are also inducible by RA in selected systems. However, their expression patterns in different cell types and a mechanistic understanding of their function is still lacking. Based on preliminary kinetic data and protein expression levels, one may predict that if CYP26A1 is expressed in the liver at even very low levels, it will be the major RA hydroxylase in this tissue. As such, it is an attractive pharmacological target for drug development when one aims to increase circulating or cellular RA concentrations. To further the understanding of how CYP26 enzymes contribute to the regulation of RA homeostasis, structural information of the CYP26s, commercially available recombinant enzymes and good specific and sensitive antibodies are needed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional properties and substrate characterization of human CYP26A1, CYP26B1, and CYP26C1 expressed by recombinant baculovirus in insect cells.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2011 Nov-Dec;64(3):258-63. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2011. PMID: 21906690
-
Cytochrome P450s in the regulation of cellular retinoic acid metabolism.Annu Rev Nutr. 2011 Aug 21;31:65-87. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-072610-145127. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21529158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Both all-trans retinoic acid and cytochrome P450 (CYP26) inhibitors affect the expression of vitamin A metabolizing enzymes and retinoid biomarkers in organotypic epidermis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2009 Aug;301(7):475-85. doi: 10.1007/s00403-009-0937-7. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009. PMID: 19294396
-
Expression and functional characterization of cytochrome P450 26A1, a retinoic acid hydroxylase.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jan 15;77(2):258-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.10.012. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18992717 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid metabolism in cancer: potential feasibility of retinoic acid metabolism blocking therapy.Med Mol Morphol. 2023 Mar;56(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s00795-022-00345-6. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Med Mol Morphol. 2023. PMID: 36592231 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of the inhibition of the retinoic acid hydroxylases CYP26A1 and CYP26B1 by xenobiotics.Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(12):1402-28. doi: 10.2174/1568026611313120004. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23688132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic acid as target for local pharmacokinetic interaction with modafinil in neural cells.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2012 Dec;262(8):697-704. doi: 10.1007/s00406-012-0309-8. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22434147
-
Direct protein-protein interactions and substrate channeling between cellular retinoic acid binding proteins and CYP26B1.FEBS Lett. 2016 Aug;590(16):2527-35. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12303. Epub 2016 Jul 28. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 27416800 Free PMC article.
-
Liposomal delivery of hydrophobic RAMBAs provides good bioavailability and significant enhancement of retinoic acid signalling in neuroblastoma tumour cells.J Drug Target. 2020 Jul;28(6):643-654. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2019.1710157. Epub 2020 Jan 14. J Drug Target. 2020. PMID: 31903789 Free PMC article.
-
Robust derivation of transplantable dopamine neurons from human pluripotent stem cells by timed retinoic acid delivery.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 1;13(1):3046. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30777-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35650213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tzimas G, Nau H. The role of metabolism and toxicokinetics in retinoid teratogenesis. Curr Pharm Des. 2001;7:803–31. - PubMed
-
- Blomhoff R, Blomhoff HK. Overview of retinoid metabolism and function. J Neurobiol. 2006;66:606–30. - PubMed
-
- Tang GW, Russell RM. 13-cis-retinoic acid is an endogenous compound in human serum. J Lipid Res. 1990;31:175–82. - PubMed
-
- Tzimas G, Collins MD, Burgin H, et al. Embryotoxic doses of vitamin A to rabbits result in low plasma but high embryonic concentrations of all-trans-retinoic acid: risk of vitamin A exposure in humans. J Nutr. 1996;126:2159–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
