Opiate-agonist induced taste aversion learning in the Fischer 344 and Lewis inbred rat strains: evidence for differential mu opioid receptor activation
- PMID: 19508878
- PMCID: PMC2752745
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2009.06.001
Opiate-agonist induced taste aversion learning in the Fischer 344 and Lewis inbred rat strains: evidence for differential mu opioid receptor activation
Abstract
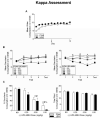
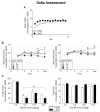
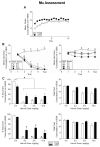
The Fischer 344 (F344) and Lewis (LEW) inbred rat strains react differently to morphine in a number of behavioral and physiological preparations, including the acquisition of aversions induced by this compound. The present experiment tested the ability of various compounds with relative selectivity at kappa, delta and mu receptor subtypes to assess the relative roles of these subtypes in mediating the differential aversive effects of morphine in the two strains. In the assessment of the role of the kappa receptor in morphine-induced aversions, animals in both strains were given access to saccharin followed by varying doses of the kappa agonist (-)-U50,488H (0.0, 0.28, 0.90 and 1.60 mg/kg). Although (-)-U50,488H induced aversions in both strains, no strain differences emerged. A separate subset of subjects was trained with the selective delta opioid agonist, SNC80 (0.0, 5.6, 10.0 and 18.0 mg/kg), and again although SNC80 induced aversions, there were no strain differences. Finally, a third subset of subjects was trained with heroin (0.0, 3.2, 5.6 and 10.0 mg/kg), a compound with activity at all three opiate receptor subtypes. Although heroin induced aversions in both strains, the aversions were significantly greater in the F344 strain, suggesting that differential activation of the mu opioid receptor likely mediates the reported strain differences in morphine-induced aversion learning. These data were discussed in terms of strain differences in opioid system functioning and the implications of such differences for other morphine-induced behavioral effects reported in F344 and LEW rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the aversive effects of peripheral mu opioid receptor agonism in Fischer 344 and Lewis rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Apr;101(2):181-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.01.001. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012. PMID: 22260873
-
Assessment of SNC 80 and naltrindole within a conditioned taste aversion design.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000 Aug;66(4):779-87. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(00)00278-1. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000. PMID: 10973516
-
Involvement of mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptor subtypes in the discriminative-stimulus effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Jun;179(4):804-12. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-2118-x. Epub 2004 Dec 24. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15619107
-
Differential effects of mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptor agonists on the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 1997 Apr 11;324(1):21-9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(97)00062-9. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9137909
-
Naloxone-induced taste aversions in opiate-naïve Lewis and Fischer 344 rat strains.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012 Apr 1;122(1-2):152-5. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.09.016. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012. PMID: 21996495
Cited by
-
Dose escalation and dose preference in extended-access heroin self-administration in Lewis and Fischer rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Mar;220(1):163-72. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2464-4. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 21894484 Free PMC article.
-
The C-2 derivatives of salvinorin A, ethoxymethyl ether Sal B and β-tetrahydropyran Sal B, have anti-cocaine properties with minimal side effects.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Aug;234(16):2499-2514. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4637-2. Epub 2017 May 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28536865 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Aversive Effects of Drugs on Their Use and Abuse.Behav Neurol. 2022 Apr 20;2022:8634176. doi: 10.1155/2022/8634176. eCollection 2022. Behav Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35496768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of cannabinoid transmission in emotional memory formation: implications for addiction and schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2014 Jun 30;5:73. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00073. eCollection 2014. Front Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25071606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoid transmission in the prelimbic cortex bidirectionally controls opiate reward and aversion signaling through dissociable kappa versus μ-opiate receptor dependent mechanisms.J Neurosci. 2013 Sep 25;33(39):15642-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1686-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24068830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrosio E, Goldberg SR, Elmer GI. Behavioral genetic investigation of the relationship between spontaneous locomotor activity and the acquisition of morphine self-administration behavior. Behav Pharmacol. 1995;6:229–37. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A, Zito KA, van der Kooy D. Peripheral receptors mediate the aversive conditioning effects of morphine in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1987;28:219–25. - PubMed
-
- Broadbent J, Muccino KJ, Cunningham CL. Ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion in 15 inbred mouse strains. Behav Neurosci. 2002;116:138–48. - PubMed
-
- Connelly CD, Martinez RP, Schupsky JJ, Porreca F, Raffa RB. Etonitazene-induced antinociception in mu1 opioid receptor deficient CXBK mice: evidence for a role for mu2 receptors in supraspinal antinociception. Life Sci. 1994;54:PL369–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

