Constitutive non-canonical NFkappaB signaling in pancreatic cancer cells
- PMID: 19502791
- PMCID: PMC2910422
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.8.16.8961
Constitutive non-canonical NFkappaB signaling in pancreatic cancer cells
Abstract
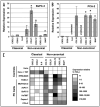
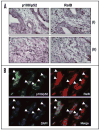
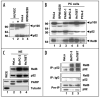
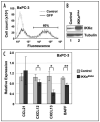
Constitutive classical NFkappaB activation has been implicated in the development of pancreatic cancer, and inhibition of classical NFkappaB signaling sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to apoptosis. However, the role of the more recently described non-canonical NFkappaB pathway has not been specifically addressed in pancreatic cancer. The non-canonical pathway requires stabilization of NIK and IKKalpha-dependent phosphorylation and processing of NFkappaB2/p100 to p52. This leads to the activation of p52-RelB heterodimers that regulate genes encoding lymphoid-specific chemokines and cytokines. We performed qRT-PCR to detect gene expression in a panel of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines (BxPC-3, PCA-2, PANC-1, Capan-1, Hs-766T, AsPC-1, MiaPACA-2) and found only modest elevation of classical NFkappaB-dependent genes. In contrast, each of the tumor cell lines displayed dramatically elevated levels of subsets of the non-canonical NFkappaB target genes CCL19, CCL21, CXCL12, CXCL13 and BAFF. Consistent with activation of the non-canonical pathway, p52 and RelB co-localized in adenocarcinoma cells in sections of pancreatic tumor tissue, and each of the tumor cell lines displayed elevated p52 levels. Furthermore, p52 and RelB co-immunoprecipitated from pancreatic cancer cells and immunoblotting revealed that NIK was stabilized and p100 was constitutively phosphorylated in a subset of the cell lines. Finally, stable overexpression of dominant negative IKKalpha significantly inhibited non-canonical target gene expression in BxPC-3 cells. These findings therefore demonstrate that the non-canonical NFkappaB pathway is constitutively active and functional in pancreatic cancer cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TRAF3 controls activation of the canonical and alternative NFkappaB by the lymphotoxin beta receptor.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 23;285(17):12971-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.076091. Epub 2010 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20185819 Free PMC article.
-
A roadmap of constitutive NF-κB activity in Hodgkin lymphoma: Dominant roles of p50 and p52 revealed by genome-wide analyses.Genome Med. 2016 Mar 17;8(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0280-5. Genome Med. 2016. PMID: 26988706 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical NFκB activation promotes chemokine expression in podocytes.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 29;6:28857. doi: 10.1038/srep28857. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27353019 Free PMC article.
-
Advancement of NF-κB Signaling Pathway: A Novel Target in Pancreatic Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 5;19(12):3890. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123890. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30563089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NFκB signalling in colorectal cancer: Examining the central dogma of IKKα and IKKβ signalling.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 12;10(12):e32904. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32904. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38975078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NLRP12 suppresses colon inflammation and tumorigenesis through the negative regulation of noncanonical NF-κB signaling.Immunity. 2012 May 25;36(5):742-54. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.03.012. Epub 2012 Apr 12. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22503542 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer: underlying mechanisms and potential targets.Front Physiol. 2014 Jan 16;4:415. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00415. eCollection 2013. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24474939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncanonical NF-κB in Cancer.Biomedicines. 2018 Jun 5;6(2):66. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6020066. Biomedicines. 2018. PMID: 29874793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RET/PTC3 oncogene activates classical NF-κB by stabilizing NIK.Oncogene. 2011 Jan 6;30(1):87-96. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.396. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 20818435 Free PMC article.
-
p52 expression enhances lung cancer progression.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 17;8(1):6078. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24488-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29666445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basseres DS, Baldwin AS. Nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene. 2006;25:6817–30. - PubMed
-
- Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature. 2006;441:431–6. - PubMed
-
- Gilmore TD, Herscovitch M. Inhibitors of NFkappaB signaling: 785 and counting. Oncogene. 2006;25:6887–99. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM. The IKK NFkappaB system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Hawke N, Baldwin AS. NFkappaB and IKK as therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:738–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
