How diverse--CD4 effector T cells and their functions
- PMID: 19482777
- PMCID: PMC2841031
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjp001
How diverse--CD4 effector T cells and their functions
Abstract
CD4 effector T cells, also called helper T (Th) cells, are the functional cells for executing immune functions. Balanced immune responses can only be achieved by proper regulation of the differentiation and function of Th cells. Dysregulated Th cell function often leads to inefficient clearance of pathogens and causes inflammatory diseases and autoimmunity. Since the establishment of the Th1-Th2 dogma in the 1980s, different lineages of effector T cells have been identified that not only promote but also suppress immune responses. Through years of collective efforts, much information was gained on the function and regulation of different subsets of Th cells. In this review, we attempt to sample the essence of what has been learnt in this field over the past two decades. We will discuss the classification and immunological functions of effector T cells, the determinants for effector T cell differentiation, as well as the relationship between different lineages of effector T cells.
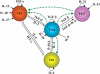
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations (*).Annu Rev Immunol. 2010;28:445-89. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101212. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20192806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic balance between master transcription factors determines the fates and functions of CD4 T cell and innate lymphoid cell subsets.J Exp Med. 2017 Jul 3;214(7):1861-1876. doi: 10.1084/jem.20170494. Epub 2017 Jun 19. J Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 28630089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Differentiation of Effector CD4+ T Helper Cell Subsets.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1960:75-84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9167-9_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30798522
-
Profiling of CD4+ T cells with epigenetic immune lineage analysis.J Immunol. 2011 Jan 1;186(1):92-102. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000960. Epub 2010 Dec 3. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21131423
-
T helper cells plasticity in inflammation.Cytometry A. 2014 Jan;85(1):36-42. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22348. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Cytometry A. 2014. PMID: 24009159 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection: specific neutrophil and cytokine levels provide increased accuracy in predicting disease severity.Paediatr Respir Rev. 2015 Sep;16(4):232-40. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 23. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2015. PMID: 26074450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prokaryotic Expression, In Vitro Biological Analysis, and In Silico Structural Evaluation of Guinea Pig IL-4.Mol Biotechnol. 2020 Feb;62(2):104-110. doi: 10.1007/s12033-019-00227-w. Mol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31758487
-
Natural killer cells for pancreatic cancer immunotherapy: Role of nanoparticles.Cancer Lett. 2023 Nov 28;579:216462. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216462. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 37924937 Free PMC article.
-
Human Th2 but not Th9 cells release IL-31 in a STAT6/NF-κB-dependent way.J Immunol. 2014 Jul 15;193(2):645-54. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301836. Epub 2014 Jun 18. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24943220 Free PMC article.
-
Androgens alter T-cell immunity by inhibiting T-helper 1 differentiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jul 8;111(27):9887-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402468111. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24958858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afkarian M., Sedy J.R., Yang J., Jacobson N.G., Cereb N., Yang S.Y., Murphy T.L., Murphy K.M. T-bet is a STAT1-induced regulator of IL-12R expression in naive CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:549–557. - PubMed
-
- Altare F., Durandy A., Lammas D., Emile J.F., Lamhamedi S., Le Deist F., Drysdale P., Jouanguy E., Doffinger R., Bernaudin F., et al. Impairment of mycobacterial immunity in human interleukin-12 receptor deficiency. Science. 1998;a 280:1432–1435. - PubMed
-
- Altare F., Lammas D., Revy P., Jouanguy E., Doffinger R., Lamhamedi S., Drysdale P., Scheel-Toellner D., Girdlestone J., Darbyshire P., et al. Inherited interleukin 12 deficiency in a child with bacille Calmette-Guerin and Salmonella enteritidis disseminated infection. J. Clin. Invest. 1998;b 102:2035–2040. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amsen D., Blander J.M., Lee G.R., Tanigaki K., Honjo T., Flavell R.A. Instruction of distinct CD4 T helper cell fates by different notch ligands on antigen-presenting cells. Cell. 2004;117:515–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

