Dynamic and combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs)
- PMID: 19471584
- PMCID: PMC2686084
- DOI: 10.1621/nrs.07005
Dynamic and combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs)
Abstract
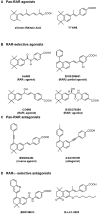
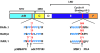
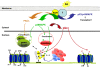
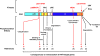
Nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARs) are transcriptional regulators controlling the expression of specific subsets of genes in a ligand-dependent manner. The basic mechanism for switching on transcription of cognate target genes involves RAR binding at specific response elements and a network of interactions with coregulatory protein complexes, the assembly of which is directed by the C-terminal ligand-binding domain of RARs. In addition to this scenario, new roles for the N-terminal domain and the ubiquitin-proteasome system recently emerged. Moreover, the functions of RARs are not limited to the regulation of cognate target genes, as they can transrepress other gene pathways. Finally, RARs are also involved in nongenomic biological activities such as the activation of translation and of kinase cascades. Here we will review these mechanisms, focusing on how kinase signaling and the proteasome pathway cooperate to influence the dynamics of RAR transcriptional activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein kinases and the proteasome join in the combinatorial control of transcription by nuclear retinoic acid receptors.Trends Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;17(6):302-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.04.003. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Trends Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17467991 Review.
-
Acinus-S' represses retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-regulated gene expression through interaction with the B domains of RARs.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Apr;28(8):2549-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01199-07. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18250153 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and retinoic acid receptors differentially control the interactions of retinoid X receptor heterodimers with ligands, coactivators, and corepressors.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;17(4):2166-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.4.2166. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9121466 Free PMC article.
-
The proteosome inhibitor MG132 attenuates retinoic acid receptor trans-activation and enhances trans-repression of nuclear factor kappaB. Potential relevance to chemo-preventive interventions with retinoids.Mol Cancer. 2004 Mar 22;3:8. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-3-8. Mol Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15035668 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear and extra-nuclear effects of retinoid acid receptors: how they are interconnected.Subcell Biochem. 2014;70:103-27. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-9050-5_6. Subcell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24962883 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective Retinoic Acid Receptor γ Agonists Promote Repair of Injured Skeletal Muscle in Mouse.Am J Pathol. 2015 Sep;185(9):2495-504. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.05.007. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26205250 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A and retinoid signaling: genomic and nongenomic effects.J Lipid Res. 2013 Jul;54(7):1761-75. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R030833. Epub 2013 Feb 24. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23440512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoproteome and Transcriptome of RA-Responsive and RA-Resistant Breast Cancer Cell Lines.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 30;11(6):e0157290. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157290. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27362937 Free PMC article.
-
All-trans retinoic acid in non-promyelocytic acute myeloid leukemia: driver lesion dependent effects on leukemic stem cells.Cell Cycle. 2020 Oct;19(20):2573-2588. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1810402. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 32900260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene profiling of head mesoderm in early zebrafish development: insights into the evolution of cranial mesoderm.Evodevo. 2019 Jul 6;10:14. doi: 10.1186/s13227-019-0128-3. eCollection 2019. Evodevo. 2019. PMID: 31312422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsayed Y., Uddin S., Mahmud N., Lekmine F., Kalvakolanu D. V., Minucci S., Bokoch G., Platanias L. C. Activation of Rac1 and the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in response to all-trans-retinoic acid. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:4012–9.. - PubMed
-
- Altucci L., Gronemeyer H. Nuclear receptors in cell life and death. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2001;12:460–8.. - PubMed
-
- Altucci L., Leibowitz M. D., Ogilvie K. M., de Lera A. R., Gronemeyer H. RAR and RXR modulation in cancer and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:793–810. - PubMed
-
- Andrau J. C., van de Pasch L., Lijnzaad P., Bijma T., Koerkamp M. G., van de Peppel J., Werner M., Holstege F. C. Genome-wide location of the coactivator mediator: Binding without activation and transient Cdk8 interaction on DNA. Mol Cell. 2006;22:179–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

