CAPS activity in priming vesicle exocytosis requires CK2 phosphorylation
- PMID: 19460754
- PMCID: PMC2707249
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.017483
CAPS activity in priming vesicle exocytosis requires CK2 phosphorylation
Abstract
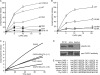
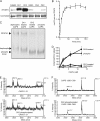
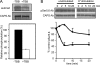
CAPS (Ca(2+)-dependent activator protein for secretion) functions in priming Ca(2+)-dependent vesicle exocytosis, but the regulation of CAPS activity has not been characterized. Here we show that phosphorylation by protein kinase CK2 is required for CAPS activity. Dephosphorylation eliminated CAPS activity in reconstituting Ca(2+)-dependent vesicle exocytosis in permeable and intact PC12 cells. Ser-5, -6, and -7 and Ser-1281 were identified by mass spectrometry as the major phosphorylation sites in the 1289 residue protein. Ser-5, -6, and -7 but not Ser-1281 to Ala substitutions abolished CAPS activity. Protein kinase CK2 phosphorylated CAPS in vitro at these sites and restored the activity of dephosphorylated CAPS. CK2 is the likely in vivo CAPS protein kinase based on inhibition of phosphorylation by tetrabromo-2-benzotriazole in PC12 cells and by the identity of in vivo and in vitro phosphorylation sites. CAPS phosphorylation by CK2 was constitutive, but the elevation of Ca(2+) in synaptosomes increased CAPS Ser-5 and -6 dephosphorylation, which terminates CAPS activity. These results identify a functionally important N-terminal phosphorylation site that regulates CAPS activity in priming vesicle exocytosis.
Figures
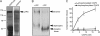


Similar articles
-
The cytosolic protein kinase CK2 phosphorylates cardiac calsequestrin in intact cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Jul;353(1-2):81-91. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0777-6. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21431367 Free PMC article.
-
CAPS and Munc13 utilize distinct PIP2-linked mechanisms to promote vesicle exocytosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Feb;25(4):508-21. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-11-0829. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24356451 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular phosphorylation of collagen XVII by ecto-casein kinase 2 inhibits ectodomain shedding.J Biol Chem. 2007 Aug 3;282(31):22737-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701937200. Epub 2007 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17545155
-
CAPS acts at a prefusion step in dense-core vesicle exocytosis as a PIP2 binding protein.Neuron. 2004 Aug 19;43(4):551-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.07.028. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 15312653
-
Nuclear export of S6K1 II is regulated by protein kinase CK2 phosphorylation at Ser-17.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 20;281(42):31188-201. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602618200. Epub 2006 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16895915
Cited by
-
Novel interactions of CAPS (Ca2+-dependent activator protein for secretion) with the three neuronal SNARE proteins required for vesicle fusion.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 12;285(46):35320-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.145169. Epub 2010 Sep 8. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20826818 Free PMC article.
-
CK2 Phosphorylation Is Required for Regulation of Syntaxin 1A Activity in Ca2+-Triggered Release in Neuroendocrine Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 17;22(24):13556. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413556. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948351 Free PMC article.
-
The priming factor CAPS1 regulates dense-core vesicle acidification by interacting with rabconnectin3β/WDR7 in neuroendocrine cells.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 14;294(24):9402-9415. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007504. Epub 2019 Apr 19. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31004036 Free PMC article.
-
CAPS and Munc13: CATCHRs that SNARE Vesicles.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013 Dec 4;4:187. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00187. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013. PMID: 24363652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Munc13 homology domain-1 in CAPS/UNC31 mediates SNARE binding required for priming vesicle exocytosis.Cell Metab. 2011 Aug 3;14(2):254-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.07.002. Cell Metab. 2011. PMID: 21803295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walent J. H., Porter B. W., Martin T. F. (1992) Cell 70, 765–775 - PubMed
-
- Ann K., Kowalchyk J. A., Loyet K. M., Martin T. F. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 19637–19640 - PubMed
-
- Grishanin R. N., Kowalchyk J. A., Klenchin V. A., Ann K., Earles C. A., Chapman E. R., Gerona R. R., Martin T. F. (2004) Neuron 43, 551–562 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

