Biomechanical forces promote embryonic haematopoiesis
- PMID: 19440194
- PMCID: PMC2782763
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08073
Biomechanical forces promote embryonic haematopoiesis
Abstract
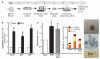
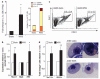
Biomechanical forces are emerging as critical regulators of embryogenesis, particularly in the developing cardiovascular system. After initiation of the heartbeat in vertebrates, cells lining the ventral aspect of the dorsal aorta, the placental vessels, and the umbilical and vitelline arteries initiate expression of the transcription factor Runx1 (refs 3-5), a master regulator of haematopoiesis, and give rise to haematopoietic cells. It remains unknown whether the biomechanical forces imposed on the vascular wall at this developmental stage act as a determinant of haematopoietic potential. Here, using mouse embryonic stem cells differentiated in vitro, we show that fluid shear stress increases the expression of Runx1 in CD41(+)c-Kit(+) haematopoietic progenitor cells, concomitantly augmenting their haematopoietic colony-forming potential. Moreover, we find that shear stress increases haematopoietic colony-forming potential and expression of haematopoietic markers in the para-aortic splanchnopleura/aorta-gonads-mesonephros of mouse embryos and that abrogation of nitric oxide, a mediator of shear-stress-induced signalling, compromises haematopoietic potential in vitro and in vivo. Collectively, these data reveal a critical role for biomechanical forces in haematopoietic development.
Figures
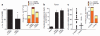
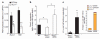
Comment in
-
Stem cells: The stress of forming blood cells.Nature. 2009 Jun 25;459(7250):1068-9. doi: 10.1038/4591068a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19553988 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Gata3 targets Runx1 in the embryonic haematopoietic stem cell niche.IUBMB Life. 2020 Jan;72(1):45-52. doi: 10.1002/iub.2184. Epub 2019 Oct 21. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 31634421 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 modulates c-Kit expression and differentiation potential in murine embryonic aorta-gonad-mesonephros haematopoiesis in vitro.Br J Haematol. 2007 Oct;139(2):321-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06795.x. Br J Haematol. 2007. PMID: 17897310 Free PMC article.
-
YAP Regulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Formation in Response to the Biomechanical Forces of Blood Flow.Dev Cell. 2020 Feb 24;52(4):446-460.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.01.006. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 32032546 Free PMC article.
-
[From the primitive to the definitive aorta: angioblasts and hemangioblasts during aorta-associated haematopoiesis].J Soc Biol. 2005;199(2):85-91. doi: 10.1051/jbio:2005009. J Soc Biol. 2005. PMID: 16485595 Review. French.
-
Role of the microenvironment of the embryonic aorta-gonad-mesonephros region in hematopoiesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;938:109-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03579.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11458497 Review.
Cited by
-
Shear stress during early embryonic stem cell differentiation promotes hematopoietic and endothelial phenotypes.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2013 Apr;110(4):1231-42. doi: 10.1002/bit.24782. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2013. PMID: 23138937 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic three-dimensional microenvironment for controlling stem cell fate.Interface Focus. 2011 Oct 6;1(5):792-803. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2011.0035. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Interface Focus. 2011. PMID: 23050083 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo imaging of haematopoietic cells emerging from the mouse aortic endothelium.Nature. 2010 Mar 4;464(7285):116-20. doi: 10.1038/nature08764. Epub 2010 Feb 14. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20154729
-
Cell sheet integrity and nanomechanical breakdown during programmed cell death.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2010 Oct;48(10):1015-22. doi: 10.1007/s11517-010-0640-z. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2010. PMID: 20535576
-
Hematopoietic responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Mar 13;79(3):187. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04220-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35284964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hove JR, et al. Intracardiac fluid forces are an essential epigenetic factor for embryonic cardiogenesis. Nature. 2003;421:172–177. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Porrero JA, Godin IE, Dieterlen-Lievre F. Potential intraembryonic hemogenic sites at pre-liver stages in the mouse. Anat. Embryol. 1995;192:425–435. - PubMed
-
- North TE, et al. Runx1 expression marks long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cells in the midgestation mouse embryo. Immunity. 2002;16:661–672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

