Bortezomib induces canonical nuclear factor-kappaB activation in multiple myeloma cells
- PMID: 19436050
- PMCID: PMC2721785
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-199604
Bortezomib induces canonical nuclear factor-kappaB activation in multiple myeloma cells
Abstract
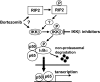
Bortezomib is a proteasome inhibitor with remarkable preclinical and clinical antitumor activity in multiple myeloma (MM) patients. The initial rationale for its use in MM was inhibition of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activity by blocking proteasomal degradation of inhibitor of kappaBalpha (IkappaBalpha). Bortezomib inhibits inducible NF-kappaB activity; however, its impact on constitutive NF-kappaB activity in MM cells has not yet been defined. In this study, we demonstrate that bortezomib significantly down-regulated IkappaBalpha expression and triggered NF-kappaB activation in MM cell lines and primary tumor cells from MM patients. Importantly, no inhibition of p65 (RelA) nuclear translocation was recognized after bortezomib treatment in a murine xenograft model bearing human MM cells. Bortezomib-induced NF-kappaB activation was mediated via the canonical pathway. Moreover, other classes of proteasome inhibitors also induced IkappaBalpha down-regulation associated with NF-kappaB activation. Molecular mechanisms whereby bortezomib induced IkappaBalpha down-regulation were further examined. Bortezomib triggered phosphorylation of IkappaB kinase (IKKbeta) and its upstream receptor-interacting protein 2, whereas IKKbeta inhibitor MLN120B blocked bortezomib-induced IkappaBalpha down-regulation and NF-kappaB activation, indicating receptor-interacting protein 2/IKKbeta signaling plays crucial role in bortezomib-induced NF-kappaB activation. Moreover, IKKbeta inhibitors enhanced bortezomib-induced cytotoxicity. Our studies therefore suggest that bortezomib-induced cytotoxicity cannot be fully attributed to inhibition of canonical NF-kappaB activity in MM cells.
Figures
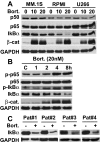
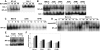
 ), 3 hours (
), 3 hours ( ) and 6 hours (■). Gene expression of Bcl-xL, CD44, IRF4, and ICAM1 was analyzed by DNA microarray.
) and 6 hours (■). Gene expression of Bcl-xL, CD44, IRF4, and ICAM1 was analyzed by DNA microarray.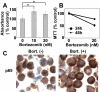


 ; 10 μM, ■) or absence (□) of MLN120B, and cell growth was assessed by MTT assay. * P < .01.
; 10 μM, ■) or absence (□) of MLN120B, and cell growth was assessed by MTT assay. * P < .01.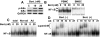
Comment in
-
Bortezomib paradigm shift in myeloma.Blood. 2009 Jul 30;114(5):931-2. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-223230. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19643992 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
IKKβ inhibitor in combination with bortezomib induces cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2014 Apr;44(4):1171-6. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2273. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24481412 Free PMC article.
-
N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide inhibits invasion, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and potentiates apoptosis through down-regulation of I(kappa)B(alpha) kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products.Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 15;65(20):9555-65. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1585. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16230421
-
The role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the biology and treatment of multiple myeloma.Semin Oncol. 2001 Dec;28(6):626-33. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(01)90036-3. Semin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11740821 Review.
-
Long-term incubation with proteasome inhibitors (PIs) induces IκBα degradation via the lysosomal pathway in an IκB kinase (IKK)-dependent and IKK-independent manner.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 8;288(45):32777-32786. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.480921. Epub 2013 Oct 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24085292 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of bortezomib in the treatment of multiple myeloma.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2007 May;2(2):128-37. doi: 10.1007/s11899-007-0018-y. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2007. PMID: 20425361 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system in a pancreatic cancer subtype with hyperactive MYC.Mol Oncol. 2020 Dec;14(12):3048-3064. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12835. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33099868 Free PMC article.
-
The Notch/Hes1 pathway sustains NF-κB activation through CYLD repression in T cell leukemia.Cancer Cell. 2010 Sep 14;18(3):268-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.08.006. Cancer Cell. 2010. PMID: 20832754 Free PMC article.
-
A Hyaluronan and Proteoglycan Link Protein 1 Matrikine: Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 in Multiple Myeloma NF-κB Activation and Drug Resistance.Mol Cancer Res. 2022 Sep 2;20(9):1456-1466. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-21-0941. Mol Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35604822 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy.J Cell Commun Signal. 2011 Jun;5(2):101-10. doi: 10.1007/s12079-011-0121-7. Epub 2011 Jan 31. J Cell Commun Signal. 2011. PMID: 21484190 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Gene Clusters in Global Pathogenesis of Clear Cell Carcinoma of the Ovary Discovered by Integrated Analysis of Transcriptomes.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jun 2;17(11):3951. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17113951. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32498447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ries LAG, Melbert D, Krapcho M, et al., editors. Bethesda MD: National Cancer Institute; 2007. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2004.
-
- Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, Tonon G, Richardson PG, Anderson KC. Understanding multiple myeloma pathogenesis in the bone marrow to identify new therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:585–598. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Greten FR. NF-κB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:749–759. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AS., Jr The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–683. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan D, Uchiyama H, Akbarali Y, et al. Multiple myeloma cell adhesion-induced interleukin-6 expression in bone marrow stromal cells involves activation of NF-κB. Blood. 1996;87:1104–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

