A resting pool of vesicles is responsible for spontaneous vesicle fusion at the synapse
- PMID: 19430474
- PMCID: PMC2738656
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2317
A resting pool of vesicles is responsible for spontaneous vesicle fusion at the synapse
Abstract
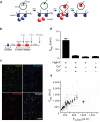
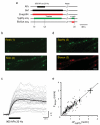
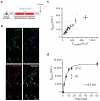
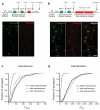
Synapses relay information through the release of neurotransmitters stored in presynaptic vesicles. The identity, kinetics and location of the vesicle pools that are mobilized by neuronal activity have been studied using a variety of techniques. We created a genetically encoded probe, biosyn, which consists of a biotinylated VAMP2 expressed at presynaptic terminals. We exploited the high-affinity interaction between streptavidin and biotin to label biosyn with fluorescent streptavidin during vesicle fusion. This approach allowed us to tag vesicles sequentially to visualize and establish the identity of presynaptic pools. Using this technique, we were able to distinguish between two different pools of vesicles in rat hippocampal neurons: one that was released in response to presynaptic activity and another, distinct vesicle pool that spontaneously fused with the plasma membrane. We found that the spontaneous vesicles belonged to a 'resting pool' that is normally not mobilized by neuronal activity and whose function was previously unknown.
Figures
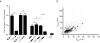
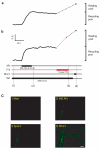
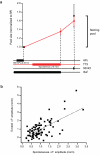
Comment in
-
Pool rules.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Jun;12(6):671-3. doi: 10.1038/nn0609-671. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19471261 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Synaptic vesicle dynamics in the mossy fiber-CA3 presynaptic terminals of mouse hippocampus.Neurosci Res. 2007 Dec;59(4):481-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2007.08.019. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17933408
-
Pool rules.Nat Neurosci. 2009 Jun;12(6):671-3. doi: 10.1038/nn0609-671. Nat Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19471261 No abstract available.
-
Synaptic vesicles recycling spontaneously and during activity belong to the same vesicle pool.Nat Neurosci. 2007 Feb;10(2):145-7. doi: 10.1038/nn1831. Epub 2007 Jan 14. Nat Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17220885
-
Vesicle pools and short-term synaptic depression: lessons from a large synapse.Trends Neurosci. 2002 Apr;25(4):206-12. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(02)02139-2. Trends Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11998689 Review.
-
The synaptic vesicle cycle.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:509-47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131412. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15217342 Review.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous Vesicle Release Is Not Tightly Coupled to Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel-Mediated Ca2+ Influx and Is Triggered by a Ca2+ Sensor Other Than Synaptotagmin-2 at the Juvenile Mice Calyx of Held Synapses.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 1;35(26):9632-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0457-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26134646 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Interplay between Inflammation and Mitochondria Aggravates Glutamate Toxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 14;25(4):2276. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042276. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell biology of Ca2+-triggered exocytosis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;22(4):496-505. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.05.001. Epub 2010 Jun 3. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20561775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel pH-Sensitive Lipid Based Exo-Endocytosis Tracers Reveal Fast Intermixing of Synaptic Vesicle Pools.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Feb 2;12:18. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00018. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29456492 Free PMC article.
-
Sharing vesicles between central presynaptic terminals: implications for synaptic function.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2010 Jun 17;2:20. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2010.00020. eCollection 2010. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21423506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Katz B. The release of neural transmitter substances. 1969
-
- Sabatini BL, Regehr WG. Timing of synaptic transmission. Annu Rev Physiol. 1999;61:521–42. - PubMed
-
- Murthy VN, Stevens CF. Reversal of synaptic vesicle docking at central synapses. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:503–7. - PubMed
-
- Geppert M, et al. Synaptotagmin I: a major Ca2+ sensor for transmitter release at a central synapse. Cell. 1994;79:717–27. - PubMed
-
- Sara Y, Virmani T, Deak F, Liu X, Kavalali ET. An isolated pool of vesicles recycles at rest and drives spontaneous neurotransmission. Neuron. 2005;45:563–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

