Noise-induced hearing loss in children: A 'less than silent' environmental danger
- PMID: 19412364
- PMCID: PMC2532893
- DOI: 10.1093/pch/13.5.377
Noise-induced hearing loss in children: A 'less than silent' environmental danger
Abstract
A review of the problems of noise-induced hearing loss in children, especially related to recreational music and the use of personal entertainment devices. The pathophysiology of noise-induced hearing loss and its associated problems (eg, tinnitus) are discussed. The evidence for an increase in noise-induced hearing loss in children and young people is reviewed. Some practical advice (for clinicians, caregivers and children) on hearing loss prevention is provided.
L’auteur analyse les problèmes reliés à la perte auditive due au bruit chez les enfants, notamment en ce qui a trait à la musique récréative et à l’utilisation d’instruments de loisir personnel. Il expose la physiopathologie de la perte auditive due au bruit et des troubles connexes (p. ex., acouphènes). Il étudie les données probantes démontrant une augmentation de la perte auditive due au bruit chez les enfants et les adolescents. Il fournit des conseils pratiques (à l’intention des cliniciens, des personnes qui s’occupent des enfants et des enfants) en vue de prévenir la perte auditive.
Keywords: Acoustic trauma; Hair cell damage; Noise-induced hearing loss; Recreational music.
Figures
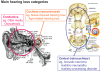
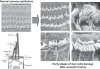



Similar articles
-
Hearing disorder from music; a neglected dysfunction.Acta Otolaryngol. 2018 Jan;138(1):21-24. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2017.1367100. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 28859531
-
WHO Environmental Noise Guidelines for the European Region: A Systematic Review on Environmental Noise and Permanent Hearing Loss and Tinnitus.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Sep 27;14(10):1139. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14101139. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28953238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Acute hearing loss and tinnitus caused by amplified recreational music].Laryngorhinootologie. 1999 Nov;78(11):614-9. doi: 10.1055/s-1999-8763. Laryngorhinootologie. 1999. PMID: 10615655 German.
-
Personal Music Players Use and Other Noise Hazards among Children 11 to 12 Years Old.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Sep 22;17(18):6934. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186934. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32971992 Free PMC article.
-
Noise-induced hearing loss.Noise Health. 2012 Nov-Dec;14(61):274-80. doi: 10.4103/1463-1741.104893. Noise Health. 2012. PMID: 23257577 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and global estimates of unsafe listening practices in adolescents and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Glob Health. 2022 Nov;7(11):e010501. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2022-010501. BMJ Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 36379592 Free PMC article.
-
Awareness About Noise Induced Hearing Loss and the Use of Unsafe Listening Practices Among Medical Students.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Aug;76(4):3458-3464. doi: 10.1007/s12070-024-04727-3. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 39130354
-
Children who say hand dryers 'hurt my ears' are correct: A real-world study examining the loudness of automated hand dryers in public places.Paediatr Child Health. 2020 Jun;25(4):216-221. doi: 10.1093/pch/pxz046. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Paediatr Child Health. 2020. PMID: 32549736 Free PMC article.
-
Variability of state school-based hearing screening protocols in the United States.J Community Health. 2013 Jun;38(3):569-74. doi: 10.1007/s10900-013-9652-6. J Community Health. 2013. PMID: 23355103
-
Acoustic noise induces attention shifts and reduces foraging performance in three-spined sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus).PLoS One. 2011 Feb 28;6(2):e17478. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017478. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21386909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harrison RV, Gordon KA, Mount RJ. Is there a critical period for cochlear implantation in congenitally deaf children? Analyses of hearing and speech perception performance after implantation. Dev Psychobiol. 2005;46:252–61. - PubMed
-
- Harrison RV, Ibrahim D, Mount RJ. Plasticity of tonotopic maps in auditory midbrain following partial cochlear damage in the developing chinchilla. Exp Brain Res. 1998;123:449–60. - PubMed
-
- Harrison RV. An animal model of auditory neuropathy. Ear Hear. 1998;19:355–61. - PubMed
-
- Morest DK, Cotanche DA. Regeneration of the inner ear as a model of neural plasticity. J Neurosci Res. 2004;78:455–60. - PubMed
-
- Breuskin I, Bodson M, Thelen N, et al. Strategies to regenerate hair cells: Identification of progenitors and critical genes. Hear Res. 2008;36:1–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
