Crystal structure of a fibroblast growth factor homologous factor (FHF) defines a conserved surface on FHFs for binding and modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels
- PMID: 19406745
- PMCID: PMC2719427
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.001842
Crystal structure of a fibroblast growth factor homologous factor (FHF) defines a conserved surface on FHFs for binding and modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels
Abstract
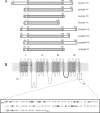
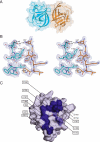
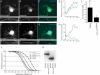
Voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav) produce sodium currents that underlie the initiation and propagation of action potentials in nerve and muscle cells. Fibroblast growth factor homologous factors (FHFs) bind to the intracellular C-terminal region of the Nav alpha subunit to modulate fast inactivation of the channel. In this study we solved the crystal structure of a 149-residue-long fragment of human FHF2A which unveils the structural features of the homology core domain of all 10 human FHF isoforms. Through analysis of crystal packing contacts and site-directed mutagenesis experiments we identified a conserved surface on the FHF core domain that mediates channel binding in vitro and in vivo. Mutations at this channel binding surface impaired the ability of FHFs to co-localize with Navs at the axon initial segment of hippocampal neurons. The mutations also disabled FHF modulation of voltage-dependent fast inactivation of sodium channels in neuronal cells. Based on our data, we propose that FHFs constitute auxiliary subunits for Navs.
Figures




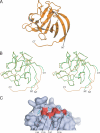

Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the ternary complex of a NaV C-terminal domain, a fibroblast growth factor homologous factor, and calmodulin.Structure. 2012 Jul 3;20(7):1167-76. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.05.001. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Structure. 2012. PMID: 22705208 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel interaction sites that determine specificity between fibroblast growth factor homologous factors and voltage-gated sodium channels.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 8;286(27):24253-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.245803. Epub 2011 May 12. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21566136 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) homologous factors share structural but not functional homology with FGFs.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 5;278(36):34226-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303183200. Epub 2003 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12815063
-
Current view on regulation of voltage-gated sodium channels by calcium and auxiliary proteins.Protein Sci. 2016 Sep;25(9):1573-84. doi: 10.1002/pro.2960. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27262167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor Homologous Factors: New Roles in Neuronal Health and Disease.Neuroscientist. 2016 Feb;22(1):19-25. doi: 10.1177/1073858414562217. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Neuroscientist. 2016. PMID: 25492945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of the ternary complex of a NaV C-terminal domain, a fibroblast growth factor homologous factor, and calmodulin.Structure. 2012 Jul 3;20(7):1167-76. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.05.001. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Structure. 2012. PMID: 22705208 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of FGF14 and NaVβ4 deletion on transient and resurgent Na current in cerebellar Purkinje neurons.J Gen Physiol. 2019 Nov 4;151(11):1300-1318. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201912390. Epub 2019 Sep 26. J Gen Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31558566 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 2 (FGF-13) associates with Nav1.7 in DRG neurons and alters its current properties in an isoform-dependent manner.Neurobiol Pain. 2019 Mar 27;6:100029. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2019.100029. eCollection 2019 Aug-Dec. Neurobiol Pain. 2019. PMID: 31223136 Free PMC article.
-
CK2 activity is required for the interaction of FGF14 with voltage-gated sodium channels and neuronal excitability.FASEB J. 2016 Jun;30(6):2171-86. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500161. Epub 2016 Feb 25. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26917740 Free PMC article.
-
Phenytoin-responsive epileptic encephalopathy with a tandem duplication involving FGF12.Neurol Genet. 2017 Jan 23;3(1):e133. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000133. eCollection 2017 Feb. Neurol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28144627 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

