Estradiol is a potent protective, restorative, and trophic factor after brain injury
- PMID: 19401955
- PMCID: PMC2846418
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0029-1216277
Estradiol is a potent protective, restorative, and trophic factor after brain injury
Abstract
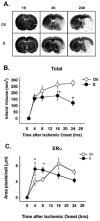
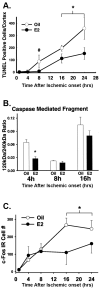
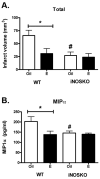
Estrogens are a group of pleiotropic steroid hormones that exhibit diverse mechanisms of action in multiple physiologic systems. Over the past 30 years, biomedical science has begun to appreciate that endogenous estrogens and their receptors display important roles beyond the reproductive system. Our growing appreciation of novel, nonreproductive functions for estrogens has fundamentally contributed to our knowledge of their role in human health and disease. Recent findings from the Women's Health Initiative have caused clinicians and scientists to question whether estrogens are protective factors or risk factors. In light of the dichotomy between basic science and clinical studies, this review will attempt to reconcile differences between them. We will focus on studies from our laboratory and others highlighting the beneficial properties of the most abundant endogenous estrogen, 17beta-estradiol, using in vivo and in vitro models of cerebral ischemia and neuronal injury. These studies demonstrate that 17beta-estradiol powerfully protects the brain using multiple molecular mechanisms that promote: (1) decreased cell death, (2) increased neurogenesis, (3) an enhancement of neurotrophic support, and (4) the suppression of proinflammatory pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex, sex steroids, and brain injury.Semin Reprod Med. 2009 May;27(3):229-39. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1216276. Epub 2009 Apr 28. Semin Reprod Med. 2009. PMID: 19401954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of neuroprotection by estrogen.Endocrine. 2006 Apr;29(2):209-15. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:29:2:209. Endocrine. 2006. PMID: 16785597 Review.
-
[Estrogens and brain].Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2012;(2):48-59. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2012. PMID: 22642178 Review. Russian.
-
Are estrogens protective or risk factors in brain injury and neurodegeneration? Reevaluation after the Women's health initiative.Endocr Rev. 2005 May;26(3):308-12. doi: 10.1210/er.2004-0014. Epub 2005 Apr 25. Endocr Rev. 2005. PMID: 15851820 Review.
-
Select estrogens within the complex formulation of conjugated equine estrogens (Premarin) are protective against neurodegenerative insults: implications for a composition of estrogen therapy to promote neuronal function and prevent Alzheimer's disease.BMC Neurosci. 2006 Mar 13;7:24. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-7-24. BMC Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16533397 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Estradiol modulates post-ischemic cerebral vascular remodeling and improves long-term functional outcome in a rat model of stroke.Brain Res. 2012 Jun 21;1461:76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.04.024. Epub 2012 Apr 21. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22572084 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences and effects of estrogenic compounds on the expression of inflammatory molecules by astrocytes exposed to the insecticide dimethoate.Neurotox Res. 2014 Apr;25(3):271-85. doi: 10.1007/s12640-013-9417-0. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Neurotox Res. 2014. PMID: 23943137
-
STX, a Novel Membrane Estrogen Receptor Ligand, Protects Against Amyloid-β Toxicity.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;51(2):391-403. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150756. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 26890746 Free PMC article.
-
Production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines during neuroinflammation: novel roles for estrogen receptors alpha and beta.Endocrinology. 2010 Oct;151(10):4916-25. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0371. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20685874 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of peripheral hormone responses to exercise on adult hippocampal neurogenesis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 24;14:1202349. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1202349. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38084331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Turgeon JL, Carr MC, Maki PM, Mendelsohn ME, Wise PM. Complex actions of sex steroids in adipose tissue, the cardiovascular system, and brain: Insights from basic science and clinical studies. Endocr Rev. 2006;27:575–605. - PubMed
-
- Behl C. Oestrogen as a neuroprotective hormone. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:433–442. - PubMed
-
- McCullough LD, Hurn PD. Estrogen and ischemic neuroprotection: an integrated view. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2003;14:228–235. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GL, Limacher M, Assaf AR, et al. Effects of conjugated equine estrogen in postmenopausal women with hysterectomy: the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;291:1701–1712. - PubMed
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2008 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2008;117:e25–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

