Phospholipase D1 is required for angiogenesis of intersegmental blood vessels in zebrafish
- PMID: 19389349
- PMCID: PMC2688691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.01.035
Phospholipase D1 is required for angiogenesis of intersegmental blood vessels in zebrafish
Abstract
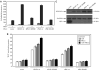
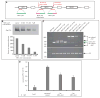
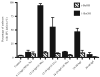
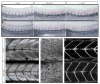
Phospholipase D (PLD) hydrolyzes phosphatidylcholine to generate phosphatidic acid and choline. Studies in cultured cells and Drosophila melanogaster have implicated PLD in the regulation of many cellular functions, including intracellular vesicle trafficking, cell proliferation and differentiation. However, the function of PLD in vertebrate development has not been explored. Here we report cloning and characterization of a zebrafish PLD1 (pld1) homolog. Like mammalian PLDs, zebrafish Pld1 contains two conservative HKD motifs. Maternally contributed pld1 transcripts are uniformly distributed in early embryo. Localized expression of pld1 is observed in the notochord during early segmentation, in the somites during later segmentation and in the liver at the larval stages. Studies in intact and cell-free preparations demonstrate evolutionary conservation of regulation. Inhibition of Pld1 expression using antisense morpholino oligonucleotides (MO) interfering with the translation or splicing of pld1 impaired intersegmental vessel (ISV) development. Incubating embryos with 1-butanol, which diverts production of phosphatidic acid to a phosphatidylalcohol, caused similar ISV defects. To determine where Pld1 is required for ISV development we performed transplantation experiments. Analyses of the mosaic Pld1 deficient embryos showed partial suppression of ISV defects in the segments containing transplanted wild-type notochord cells but not in the ones containing wild-type somitic cells. These results provide the first evidence that function of Pld1 in the developing notochord is essential for vascular development in vertebrates.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Knockdown of zebrafish crim1 results in a bent tail phenotype with defects in somite and vascular development.Mech Dev. 2006 Apr;123(4):277-87. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2006.01.003. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Mech Dev. 2006. PMID: 16524703
-
Patterning of angiogenesis in the zebrafish embryo.Development. 2002 Feb;129(4):973-82. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.4.973. Development. 2002. PMID: 11861480
-
Essential and overlapping roles for laminin alpha chains in notochord and blood vessel formation.Dev Biol. 2006 Jan 1;289(1):64-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.10.006. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16321372
-
[Wave and somite segmentation: a view from zebrafish genetic analyses].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2002 Dec;47(15):2017-23. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2002. PMID: 12486933 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Zebrafish genetics and formation of embryonic vasculature.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005;71:53-81. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(05)71002-4. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 16344102 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipidomic profiling in mouse brain reveals differences between ages and genders, with smaller changes associated with alpha-synuclein genotype.J Neurochem. 2009 Oct;111(1):15-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06290.x. Epub 2009 Jul 17. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19627450 Free PMC article.
-
Functional regulation of phospholipase D expression in cancer and inflammation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Aug 15;289(33):22575-22582. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R114.569822. Epub 2014 Jul 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24990948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zebrafish WNK lysine deficient protein kinase 1 (wnk1) affects angiogenesis associated with VEGF signaling.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 29;9(8):e106129. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106129. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25171174 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of phospholipase D2 impairs VEGF-induced angiogenesis.BMB Rep. 2016 Mar;49(3):191-6. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.3.219. BMB Rep. 2016. PMID: 26818087 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferative and metastatic roles for Phospholipase D in mouse models of cancer.Adv Biol Regul. 2018 Jan;67:134-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2017.11.004. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Adv Biol Regul. 2018. PMID: 29154090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beattie CE, Granato M, Kuwada JY. Cellular, genetic and molecular mechanisms of axonal guidance in the zebrafish. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2002;40:252–69. - PubMed
-
- Brown HA, Gutowski S, Moomaw CR, Slaughter C, Sternweis PC. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-dependent regulatory protein, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Cell. 1993;75:1137–44. - PubMed
-
- Brown HA, Henage LG, Preininger AM, Xiang Y, Exton JH. Biochemical analysis of phospholipase D. Methods Enzymol. 2007;434:49–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

