Human leucocyte antigen (HLA) expression of primary trophoblast cells and placental cell lines, determined using single antigen beads to characterize allotype specificities of anti-HLA antibodies
- PMID: 19368562
- PMCID: PMC2678179
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03019.x
Human leucocyte antigen (HLA) expression of primary trophoblast cells and placental cell lines, determined using single antigen beads to characterize allotype specificities of anti-HLA antibodies
Abstract
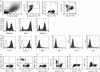
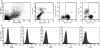
Human trophoblast cells express an unusual repertoire of human leucocyte antigen (HLA) molecules which has been difficult to define. Close homology between and extreme polymorphism at the classical HLA class-I (HLA-I) loci has made it difficult to generate locus-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). The problem of defining an antibody's reactivity against the thousands of existing HLA-I allotypes has often made it impossible to determine the HLA bound by a mAb in biological samples from a normal outbred population. Here we have used commercially available beads coated with individual HLA-I to characterize experimentally the reactivity of nine mAb against 96 common HLA-I allotypes. In conjunction with donor HLA-I genotyping, we could then define the specific HLA molecules bound by these antibodies in normal individuals. We used this approach to analyse the HLA expression of primary trophoblast cells from normal pregnancies; the choriocarcinoma cells JEG-3 and JAR; and the placental cell lines HTR-8/SVneo, Swan-71 and TEV-1. We confirm that primary villous trophoblast cells are HLA null whereas extravillous trophoblast cells express HLA-C, HLA-G and HLA-E, but not HLA-A, HLA-B or HLA-DR molecules in normal pregnancy. Tumour-derived JEG-3 and JAR cells reflect extravillous and villous trophoblast HLA phenotypes, respectively, but the HLA repertoire of the in vitro derived placental cell lines is not representative of either in vivo trophoblast phenotype. This study raises questions regarding the validity of using the placental cell lines that are currently available as model systems for immunological interactions between fetal trophoblast and maternal leucocytes bearing receptors for HLA molecules.
Figures




Similar articles
-
HLA Class I protein expression in the human placenta.Early Pregnancy (Cherry Hill). 2001 Jan;5(1):67-9. Early Pregnancy (Cherry Hill). 2001. PMID: 11753519
-
Expression of HLA class I molecules in human first trimester and term placenta trophoblast.Cell Tissue Res. 1996 Dec;286(3):439-47. doi: 10.1007/s004410050713. Cell Tissue Res. 1996. PMID: 8929346
-
Calreticulin associates with non-HLA-A,-B class I proteins in the human choriocarcinoma cell lines JEG-3 and BeWo.Immunology. 1998 Mar;93(3):437-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1998.00439.x. Immunology. 1998. PMID: 9640257 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological relationship between the mother and the fetus.Int Rev Immunol. 2002 Nov-Dec;21(6):471-95. doi: 10.1080/08830180215017. Int Rev Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12650238 Review.
-
Antigen expression by trophoblast populations in the human placenta and their possible immunobiological relevance.Placenta. 1985 Mar-Apr;6(2):127-40. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(85)80063-1. Placenta. 1985. PMID: 3895220 Review.
Cited by
-
Considerations to Model Heart Disease in Women with Preeclampsia and Cardiovascular Disease.Cells. 2021 Apr 14;10(4):899. doi: 10.3390/cells10040899. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33919808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virtual crossmatching reveals upregulation of placental HLA-Class II in chronic histiocytic intervillositis.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 12;14(1):18714. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69315-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39134702 Free PMC article.
-
Placentation in Equids.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2021;234:91-128. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-77360-1_6. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34694479
-
Ex vivo functional responses to HLA-G differ between blood and decidual NK cells.Mol Hum Reprod. 2011 Sep;17(9):577-86. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gar022. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Mol Hum Reprod. 2011. PMID: 21471023 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Specific Education of Decidual NK Cells.J Immunol. 2015 Oct 1;195(7):3026-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501229. Epub 2015 Aug 28. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26320253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moffett A, Loke C. Immunology of placentation in eutherian mammals. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:584–94. - PubMed
-
- Parham P. MHC class I molecules and KIRs in human history, health and survival. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:201–14. - PubMed
-
- Loke YW, King A. Human Implantation: Cell Biology and Immunology. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 1995.
-
- Moffett-King A. Natural killer cells and pregnancy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:656–663. - PubMed
-
- Apps R, Gardner L, Moffett A. A critical look at HLA-G. Trends Immunol. 2008;29:313–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

