Clock genes, intestinal transport and plasma lipid homeostasis
- PMID: 19349191
- PMCID: PMC4544755
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.01.001
Clock genes, intestinal transport and plasma lipid homeostasis
Abstract
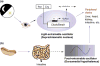
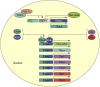
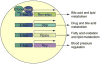
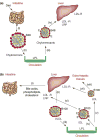
Light and food are two major environmental factors that impact daily life. Light entrainment is centrally controlled by suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus. Food entrainment might require cooperation between the intestine and dorsomedial hypothalamus. Clock genes that are essential for light entrainment also play a part in food entrainment. Understanding the role of clock genes in the entrainment of intestinal functions, as well as in gut-brain communication during food entrainment, will enhance our understanding of gastrointestinal and metabolic disorders. This review highlights recent studies examining light- and food-entrained regulation of plasma lipids and of various intestinal activities and offers insight into the role of the intestine in food entrainment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clock is important for food and circadian regulation of macronutrient absorption in mice.J Lipid Res. 2009 Sep;50(9):1800-13. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M900085-JLR200. Epub 2009 Apr 22. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19387090 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian regulators of intestinal lipid absorption.J Lipid Res. 2015 Apr;56(4):761-70. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R051573. Epub 2014 Jul 23. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 25057097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Light-entrained and brain-tuned circadian circuits regulate ILC3s and gut homeostasis.Nature. 2019 Oct;574(7777):254-258. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1579-3. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31534216 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of light and temperature in the regulation of circadian gene expression in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2007 Apr 6;3(4):e54. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030054. PLoS Genet. 2007. PMID: 17411344 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology of food anticipatory circadian rhythms.Physiol Behav. 2011 Sep 26;104(4):535-45. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.04.015. Epub 2011 Apr 20. Physiol Behav. 2011. PMID: 21527266 Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian Clock Regulation on Lipid Metabolism and Metabolic Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1276:53-66. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-6082-8_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32705594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intermittent Hypoxia and Hypercapnia Alter Diurnal Rhythms of Luminal Gut Microbiome and Metabolome.mSystems. 2021 Jun 29;6(3):e0011621. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00116-21. Online ahead of print. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34184915 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-30c reduces hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis in mice by decreasing lipid synthesis and lipoprotein secretion.Nat Med. 2013 Jul;19(7):892-900. doi: 10.1038/nm.3200. Epub 2013 Jun 9. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23749231 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism as an integral cog in the mammalian circadian clockwork.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Jul-Aug;48(4):317-31. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.786672. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23594144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronodisruption and Gut Microbiota: Triggering Glycemic Imbalance in People with Type 2 Diabetes.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 23;16(5):616. doi: 10.3390/nu16050616. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474745 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

