Rat cytomegalovirus infection depletes MHC II in bone marrow derived dendritic cells
- PMID: 19349057
- PMCID: PMC2749604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.02.050
Rat cytomegalovirus infection depletes MHC II in bone marrow derived dendritic cells
Abstract
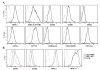
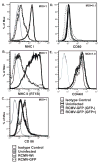
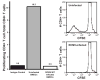
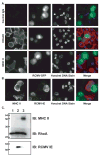
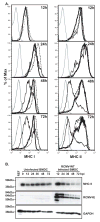
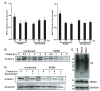
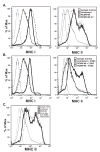
While cytomegalovirus (CMV) infects and replicates in a multitude of cell types, the ability of the virus to replicate in antigen presenting cells (APCs) is believed to play a critical role in the viral dissemination and latency. CMV infection of APCs and manipulation of their function are important areas of investigation. CMV down regulation of MHC II is reportedly mediated by the HCMV proteins US2, US3, UL83, UL111a (vIL10) or through the induction of cellular IL10. In this study, we demonstrate that rat CMV (RCMV) significantly reduces MHC II expression neither by mechanisms that do not involve orthologues of the known HCMV genes nor by an increase in cellular IL10. Rat bone marrow derived dendritic cells (BMDC) were highly susceptible to infection with RCMV and a recombinant RCMV expressing eGFP. RCMV infection of BMDCs depleted both surface and intracellular MHC II to nearly undetectable levels as well as reduced surface expression of MHC I. The effect on MHC II only occurred in the infected GFP positive cells and is mediated by an immediate early or early viral gene product. Furthermore, treatment of uninfected immature DCs with virus-free conditioned supernatants from infected cells failed to down regulate MHC II. RCMV depletion of MHC II was sensitive to treatment with lysosomal inhibitors but not proteasomal inhibitors suggesting that the mechanism of RCMV-mediated down regulation of MHC II occurs through endocytic degradation. Since RCMV does not encode homologues of US2, US3, UL83 or UL111a, these data indicate a novel mechanism for RCMV depletion of MHC II.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of the MHC class II antigen presentation pathway by human cytomegalovirus.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002;269:101-15. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59421-2_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12224504 Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus infection interferes with major histocompatibility complex type II maturation and endocytic proteases in dendritic cells at multiple levels.J Gen Virol. 2008 Oct;89(Pt 10):2427-2436. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.2008/001610-0. J Gen Virol. 2008. PMID: 18796710
-
Cytomegalovirus antigen expression, endothelial cell proliferation, and intimal thickening in rat cardiac allografts after cytomegalovirus infection.Circulation. 1995 Nov 1;92(9):2594-604. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.9.2594. Circulation. 1995. PMID: 7586362
-
Human Macrophages Escape Inhibition of Major Histocompatibility Complex-Dependent Antigen Presentation by Cytomegalovirus and Drive Proliferation and Activation of Memory CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 May 25;9:1129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01129. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29887865 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus infection of immature dendritic cells and macrophages.Intervirology. 1999;42(5-6):365-72. doi: 10.1159/000053973. Intervirology. 1999. PMID: 10702719 Review.
Cited by
-
Rat cytomegalovirus efficiently replicates in dendritic cells and induces changes in their transcriptional profile.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 23;14:1192057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1192057. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38077365 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus immune evasion by perturbation of endosomal trafficking.Cell Mol Immunol. 2015 Mar;12(2):154-69. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.85. Epub 2014 Sep 29. Cell Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25263490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytomegalovirus Infection of the Rat Developing Brain In Utero Prominently Targets Immune Cells and Promotes Early Microglial Activation.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 29;11(7):e0160176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160176. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27472761 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence-based laser capture microscopy technology facilitates identification of critical in vivo cytomegalovirus transcriptional programs.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1119:217-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-788-4_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24639226 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular distribution of CD200 receptor in rats and its interaction with cytomegalovirus e127 protein.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2018 Nov;207(5-6):307-318. doi: 10.1007/s00430-018-0552-3. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30032349
References
-
- Andrews DM, Andoniou CE, Granucci F, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Degli-Esposti MA. Infection of dendritic cells by murine cytomegalovirus induces functional paralysis. Nat Immunol. 2001;2(11):1077–84. - PubMed
-
- Cebulla CM, Miller DM, Zhang Y, Rahill BM, Zimmerman P, Robinson JM, Sedmak DD. Human cytomegalovirus disrupts constitutive MHC class II expression. J Immunol. 2002;169(1):167–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL071695-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071695/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL65754/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI21640/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL066238/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI021640/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI021640/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083194-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083194-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL71695/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI021640-24/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065754-08/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085451/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL083194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 66238-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065754/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI07472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083194-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083194-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

