The effect of tai chi on knee osteoarthritis pain in cognitively impaired elders: pilot study
- PMID: 19345855
- PMCID: PMC2748759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2007.11.002
The effect of tai chi on knee osteoarthritis pain in cognitively impaired elders: pilot study
Abstract
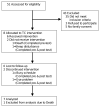
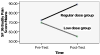
This article reports a pilot study of the effect of tai chi (TC), a pharmacological adjunct and mild aerobic exercise, on osteoarthritic knee pain in elders with cognitive impairment (CI). The TC program included a warm-up, 12-form Sun-style TC, and a cool-down period, for a total of 20-40 minutes per session, twice a week for 15 weeks. The results showed no significant differences in knee pain after the TC intervention in 7 elders with CI. However, more minutes of TC attendance were related to improved pain scores (Spearman's rho=.78, P < .05). Greater accuracy in TC performance was also correlated with improvements in pain scores (Spearman's rho = .70, P=.08). Of 4 elders who participated in TC practice regularly (more than 20 sessions), 3 showed clinically important improvements, but 3 elders who participated in no sessions or only a few sessions showed no improvement.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A pilot cluster-randomized trial of a 20-week Tai Chi program in elders with cognitive impairment and osteoarthritic knee: effects on pain and other health outcomes.J Pain Symptom Manage. 2013 Apr;45(4):660-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2012.04.009. Epub 2012 Sep 24. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2013. PMID: 23017610 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A supplemental report to a randomized cluster trial of a 20-week Sun-style Tai Chi for osteoarthritic knee pain in elders with cognitive impairment.Complement Ther Med. 2015 Aug;23(4):570-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Complement Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26275650 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Teaching Tai Chi to elders with osteoarthritis pain and mild cognitive impairment.Am J Recreat Ther. 2011 Winter;10(1):11-16. Am J Recreat Ther. 2011. PMID: 25242898 Free PMC article.
-
Tai chi as a balance improvement exercise for older adults: a systematic review.J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2010 Jul-Sep;33(3):103-9. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2010. PMID: 21155504 Review.
-
Review of Tai Chi as an effective exercise on falls prevention in elderly.Res Sports Med. 2012 Jan;20(1):37-58. doi: 10.1080/15438627.2012.634697. Res Sports Med. 2012. PMID: 22242736 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Movement-Based Mind-Body Interventions to Guide the Implementation of Osteoarthritis Exercise Programs: A Descriptive Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Altern Complement Med. 2021 May;27(5):442-457. doi: 10.1089/acm.2020.0420. Epub 2021 Apr 27. J Altern Complement Med. 2021. PMID: 33902322 Free PMC article.
-
Mind-Body Therapies and Osteoarthritis of the Knee.Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2009 Nov 1;5(4):204-211. doi: 10.2174/157339709790192512. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2009. PMID: 21151770 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Taichi Practice on Attenuating Bone Mineral Density Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Sep 1;14(9):1000. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14091000. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28862661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pilot cluster-randomized trial of a 20-week Tai Chi program in elders with cognitive impairment and osteoarthritic knee: effects on pain and other health outcomes.J Pain Symptom Manage. 2013 Apr;45(4):660-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2012.04.009. Epub 2012 Sep 24. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2013. PMID: 23017610 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Complementary and alternative exercises for management of osteoarthritis.Arthritis. 2011;2011:364319. doi: 10.1155/2011/364319. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Arthritis. 2011. PMID: 22046516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell AJ, Busby WJ, Robertson MC, et al. Disease, impairment, disability and social handicap: a community based study of people aged 70 years and over. Disabil Rehabil. 1994;16:72–9. - PubMed
-
- Felson DT, Naimark A, Anderson J, et al. The prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the elderly: the Framingham Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum. 1987;30:914–8. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Xu L, Nevitt MC, et al. Comparison of the prevalence of knee osteoarthritis between the elderly Chinese population in Beijing and whites in the United States: the Beijing Osteoarthritis Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2065–71. - PubMed
-
- Jordan J, Luta G, Renner J, et al. Knee pain and knee osteoarthritis severity in self-reported task specific disability: the Johnston County Osteoarthritis Project. J Rheumatol. 1997;24:1344–9. - PubMed
-
- Shah KR, Carr D, Roe CM, et al. Impaired physical performance and the assessment of dementia of the Alzheimer type. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2004;18:112–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical