beta2 Adrenergic receptor activation induces microglial NADPH oxidase activation and dopaminergic neurotoxicity through an ERK-dependent/protein kinase A-independent pathway
- PMID: 19330844
- PMCID: PMC3608678
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.20873
beta2 Adrenergic receptor activation induces microglial NADPH oxidase activation and dopaminergic neurotoxicity through an ERK-dependent/protein kinase A-independent pathway
Abstract
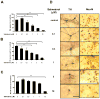
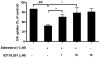
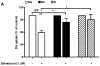
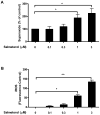
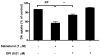
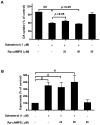
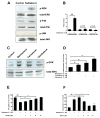
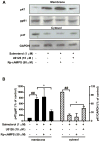
Activation of the beta2 adrenergic receptor (beta2AR) on immune cells has been reported to possess anti-inflammatory properties, however, the pro-inflammatory properties of beta2AR activation remain unclear. In this study, using rat primary mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures, we report that salmeterol, a long-acting beta2AR agonist, selectively induces dopaminergic (DA) neurotoxicity through its ability to activate microglia. Salmeterol selectively increased the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by NADPH oxidase (PHOX), the major superoxide-producing enzyme in microglia. A key role of PHOX in mediating salmeterol-induced neurotoxicity was demonstrated by the inhibition of DA neurotoxicity in cultures pretreated with diphenylene-iodonium (DPI), an inhibitor of PHOX activity. Mechanistic studies revealed the activation of microglia by salmeterol results in the selective phosphorylation of ERK, a signaling pathway required for the translocation of the PHOX cytosolic subunit p47(phox) to the cell membrane. Furthermore, we found ERK inhibition, but not protein kinase A (PKA) inhibition, significantly abolished salmeterol-induced superoxide production, p47(phox) translocation, and its ability to mediate neurotoxicity. Together, these findings indicate that beta2AR activation induces microglial PHOX activation and DA neurotoxicity through an ERK-dependent/PKA-independent pathway.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microglial MAC1 receptor and PI3K are essential in mediating β-amyloid peptide-induced microglial activation and subsequent neurotoxicity.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Jan 13;8(1):3. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21232086 Free PMC article.
-
Formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity via microglial activation: a mediator between peripheral infection and neurodegeneration?Environ Health Perspect. 2008 May;116(5):593-8. doi: 10.1289/ehp.11031. Environ Health Perspect. 2008. PMID: 18470306 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrafine carbon particles promote rotenone-induced dopamine neuronal loss through activating microglial NADPH oxidase.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 May 1;322:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28283350
-
Squamosamide derivative FLZ protects dopaminergic neurons against inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration through the inhibition of NADPH oxidase activity.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 May 28;5:21. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-21. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18507839 Free PMC article.
-
The role of D1 dopamine receptors and phospho-ERK in mediating cytotoxicity. Commentary.Neurotox Res. 2005;7(3):179-81. doi: 10.1007/BF03036447. Neurotox Res. 2005. PMID: 15897152 Review.
Cited by
-
β2-Adrenoceptor involved in smoking-induced airway mucus hypersecretion through β-arrestin-dependent signaling.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 6;9(6):e97788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097788. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24905583 Free PMC article.
-
ROS-mediated regulation of β2AR function: Does oxidation play a meaningful role towards β2-agonist tachyphylaxis in airway obstructive diseases?Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Aug;226:116403. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116403. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38945277 Review.
-
Stress and brain immunity: Microglial homeostasis through hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal gland axis and sympathetic nervous system.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020 Jul 23;7:100111. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100111. eCollection 2020 Aug. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020. PMID: 34589871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglial activation and chronic neurodegeneration.Neurotherapeutics. 2010 Oct;7(4):354-65. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2010.05.014. Neurotherapeutics. 2010. PMID: 20880500 Free PMC article.
-
Agonists and hydrogen peroxide mediate hyperoxidation of β2-adrenergic receptor in airway epithelial cells: Implications for tachyphylaxis to β2-agonists in constrictive airway disorders.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec;168:115763. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115763. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37865997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson MJ, Walters J, Walters EH. Adverse effects of beta-agonists: are they clinically relevant? Am J Respir Med. 2003;2(4):287–97. - PubMed
-
- Block ML, Hong JS. Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: Multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;76(2):77–98. - PubMed
-
- Cheepsunthorn P, Radov L, Menzies S, Reid J, Connor JR. Characterization of a novel brain-derived microglial cell line isolated from neonatal rat brain. Glia. 2001;35(1):53–62. - PubMed
-
- Christensen JD, Hansen EW, Frederiksen C, Molris M, Moesby L. Adrenaline influences the release of interleukin-6 from murine pituicytes: role of beta2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;378(1):143–8. - PubMed
-
- Daaka Y, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ. Switching of the coupling of the beta2-adrenergic receptor to different G proteins by protein kinase A. Nature. 1997;390(6655):88–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

