Origin and function of ubiquitin-like proteins
- PMID: 19325621
- PMCID: PMC2819001
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07958
Origin and function of ubiquitin-like proteins
Abstract
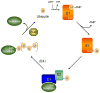
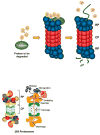
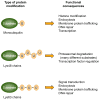
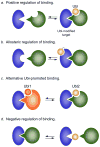
Eukaryotic proteins can be modified through attachment to various small molecules and proteins. One such modification is conjugation to ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins (UBLs), which controls an enormous range of physiological processes. Bound UBLs mainly regulate the interactions of proteins with other macromolecules, for example binding to the proteasome or recruitment to chromatin. The various UBL systems use related enzymes to attach specific UBLs to proteins (or other molecules), and most of these attachments are transient. There is increasing evidence suggesting that such UBL-protein modification evolved from prokaryotic sulphurtransferase systems or related enzymes. Moreover, proteins similar to UBL-conjugating enzymes and UBL-deconjugating enzymes seem to have already been widespread at the time of the last common ancestor of eukaryotes, suggesting that UBL-protein conjugation did not first evolve in eukaryotes.
Figures
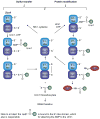
Similar articles
-
Structure and evolution of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-related domains.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;832:15-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-474-2_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22350875
-
The ligation systems for ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins.Mol Cells. 1998 Oct 31;8(5):503-12. Mol Cells. 1998. PMID: 9856335 Review.
-
Rhodanese-Like Domain Protein UbaC and Its Role in Ubiquitin-Like Protein Modification and Sulfur Mobilization in Archaea.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jul 10;201(15):e00254-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00254-19. Print 2019 Aug 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31085691 Free PMC article.
-
Integral UBL domain proteins: a family of proteasome interacting proteins.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Apr;15(2):247-59. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.12.006. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15209385 Review.
-
Specific and covalent targeting of conjugating and deconjugating enzymes of ubiquitin-like proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Jan;24(1):84-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.1.84-95.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14673145 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In silico analysis of ubiquitin/ubiquitin-like modifiers and their conjugating enzymes in Entamoeba species.Parasitol Res. 2012 Jul;111(1):37-51. doi: 10.1007/s00436-011-2799-0. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Parasitol Res. 2012. PMID: 22246365
-
Emerging roles of non-histone protein crotonylation in biomedicine.Cell Biosci. 2021 May 31;11(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00616-2. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34059135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin specific peptidase 38 epigenetically regulates KLF transcription factor 5 to augment malignant progression of lung adenocarcinoma.Oncogene. 2024 Apr;43(16):1190-1202. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-02985-7. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38409551
-
Update on sumoylation: defining core components of the plant SUMO conjugation system by phylogenetic comparison.New Phytol. 2012 Jul;195(1):23-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04135.x. New Phytol. 2012. PMID: 22799003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A general chemical ligation approach towards isopeptide-linked ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like assay reagents.Chembiochem. 2012 Jan 23;13(2):293-7. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201100706. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Chembiochem. 2012. PMID: 22213387 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hochstrasser M. Evolution and function of ubiquitin-like protein-conjugation systems. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:E153–E157. - PubMed
-
- Pickart CM. Mechanisms Underlying Ubiquitination. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:503–533. - PubMed
-
- Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M. Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:159–180. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadhyay D, Riezman H. Proteasome-independent functions of ubiquitin in endocytosis and signaling. Science. 2007;315:201–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

