Expression of CCN family of genes in human skin in vivo and alterations by solar-simulated ultraviolet irradiation
- PMID: 19319669
- PMCID: PMC2686751
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-009-0044-8
Expression of CCN family of genes in human skin in vivo and alterations by solar-simulated ultraviolet irradiation
Abstract
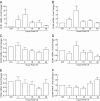
The CCN family of proteins is involved in diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, migration, angiogenesis, and regulation of extracellular matrix. We have investigated expression of CCN family genes and alternations induced by solar-simulated ultraviolet irradiation in human skin in vivo. Transcripts of all six CCN genes were expressed in human skin in vivo. CCN5 was most abundantly expressed followed by CCN2>CCN3>CCN1>CCN4>CCN6. Solar-simulated ultraviolet irradiation increased mRNA expression of CCN1 and CCN2. In contrast, mRNA levels of CCN3, CCN4, CCN5, and CCN6, were reduced. Knowledge gained from this study provides the foundation to explore the functional roles of CCN gene products in cutaneous biology and responses to solar ultraviolet irradiation.
Figures
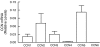
Similar articles
-
Spatial-temporal modulation of CCN proteins during wound healing in human skin in vivo.J Cell Commun Signal. 2011 Mar;5(1):69-80. doi: 10.1007/s12079-010-0114-y. Epub 2011 Jan 11. J Cell Commun Signal. 2011. PMID: 21484592 Free PMC article.
-
Temperal and spatial expression of CCN1, CCN3, CCN4, CCN5 and CCN6 proteins in the developing postnatal teeth.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jun;17(2):275-285. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00758-7. Epub 2023 May 9. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37160590 Free PMC article.
-
The CCN proteins: important signaling mediators in stem cell differentiation and tumorigenesis.Histol Histopathol. 2010 Jun;25(6):795-806. doi: 10.14670/HH-25.795. Histol Histopathol. 2010. PMID: 20376786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CCN family of genes: a perspective on CCN biology and therapeutic potential.J Cell Commun Signal. 2007 Dec;1(3-4):159-64. doi: 10.1007/s12079-008-0022-6. Epub 2008 Jun 21. J Cell Commun Signal. 2007. PMID: 18568428 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CCN Proteins in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4340. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094340. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming the challenges of studying conservation physiology in large whales: a review of available methods.Conserv Physiol. 2013 May 15;1(1):cot006. doi: 10.1093/conphys/cot006. eCollection 2013. Conserv Physiol. 2013. PMID: 27293590 Free PMC article.
-
CCN5: biology and pathophysiology.J Cell Commun Signal. 2010 Oct;4(3):119-30. doi: 10.1007/s12079-010-0098-7. Epub 2010 Sep 21. J Cell Commun Signal. 2010. PMID: 21063502 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidant exposure induces cysteine-rich protein 61 (CCN1) via c-Jun/AP-1 to reduce collagen expression in human dermal fibroblasts.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 23;9(12):e115402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115402. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25536346 Free PMC article.
-
Matricellular proteins in cutaneous wound healing.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 24;10:1073320. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1073320. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36506087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial-temporal modulation of CCN proteins during wound healing in human skin in vivo.J Cell Commun Signal. 2011 Mar;5(1):69-80. doi: 10.1007/s12079-010-0114-y. Epub 2011 Jan 11. J Cell Commun Signal. 2011. PMID: 21484592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1002/jcb.21262', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21262'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17340618', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17340618/'}]}
- Bleau A, Planque N, Lazar N, Zambelli D, Ori A, Quan T et al (2007) Antiproliferative activity of CCN3: involvement of the C-terminal module and post-translational regulation. J Cell Biochem 101:1475–1491 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1083/jcb.114.6.1285', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.114.6.1285'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2289134', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2289134/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '1654338', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1654338/'}]}
- Bradham D, Igarashi A, Potter R, Grotendorst G (1991) Connective tissue growth factor: a cysteine-rich mitogen secreted by human vascular endothelial cells is related to the SRC-induced immediate early gene product CEF-10. J Cell Biol 114:1285–1294 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1210/er.20.2.189', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1210/er.20.2.189'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10204117', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10204117/'}]}
- Brigstock D (1999) The connective tissue growth factor/Cysteine-rich 61/nephroblastoma overexpressed (CCN) family. Endocrine Rev 20:189–206 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/mp.56.2.127', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/mp.56.2.127'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1187305', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1187305/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '12665631', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12665631/'}]}
- Brigstock D, Goldschmeding R, Katsube K-I, Lam S-T, Lau L, Lyons K et al (2003) Proposal of a unified CCN nomenclature. Mol Pathol 56:127–128 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1074/jbc.M107666200', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m107666200'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11584015', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11584015/'}]}
- Chen C-C, Mo F-E, Lau L (2001) The angiogenic factor Cyr61 activates a genetic program for wound healing in human skin fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 276:47329–47337 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

