A dialogue between the hypoxia-inducible factor and the tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 19308685
- PMCID: PMC2654353
- DOI: 10.1007/s12307-008-0006-3
A dialogue between the hypoxia-inducible factor and the tumor microenvironment
Abstract
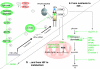
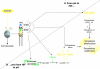
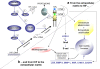
The hypoxia-inducible factor is the key protein responsible for the cellular adaptation to low oxygen tension. This transcription factor becomes activated as a result of a drop in the partial pressure of oxygen, to hypoxic levels below 5% oxygen, and targets a panel of genes involved in maintenance of oxygen homeostasis. Hypoxia is a common characteristic of the microenvironment of solid tumors and, through activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor, is at the center of the growth dynamics of tumor cells. Not only does the microenvironment impact on the hypoxia-inducible factor but this factor impacts on microenvironmental features, such as pH, nutrient availability, metabolism and the extracellular matrix. In this review we discuss the influence the tumor environment has on the hypoxia-inducible factor and outline the role of this factor as a modulator of the microenvironment and as a powerful actor in tumor remodeling. From a fundamental research point of view the hypoxia-inducible factor is at the center of a signaling pathway that must be deciphered to fully understand the dynamics of the tumor microenvironment. From a translational and pharmacological research point of view the hypoxia-inducible factor and its induced downstream gene products may provide information on patient prognosis and offer promising targets that open perspectives for novel "anti-microenvironment" directed therapies.
Figures
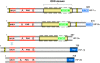
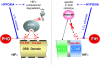
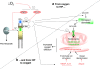
 , stimulation;
, stimulation;  , inhibition;
, inhibition;  , interaction
, interaction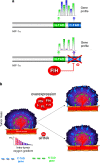

Similar articles
-
Cell metabolism under microenvironmental low oxygen tension levels in stemness, proliferation and pluripotency.Curr Mol Med. 2015;15(4):343-59. doi: 10.2174/1566524015666150505160406. Curr Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25941818
-
Perspectives on Hypoxia Signaling in Tumor Stroma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 20;13(12):3070. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123070. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia inducible factors regulate hepatitis B virus replication by activating the basal core promoter.J Hepatol. 2021 Jul;75(1):64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.12.034. Epub 2021 Jan 29. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33516779 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) in the tumor microenvironment: friend or foe?Sci China Life Sci. 2017 Oct;60(10):1114-1124. doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9178-y. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Sci China Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 29039125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The oxygen sensor factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 controls expression of distinct genes through the bifunctional transcriptional character of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha.Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 1;66(7):3688-98. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4564. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16585195
Cited by
-
Hypoxia inducible factor 1α-mediated LOX expression correlates with migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer.Int J Oncol. 2013 May;42(5):1578-88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1878. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23545606 Free PMC article.
-
Immature myeloid cells are critical for enhancing bone fracture healing through angiogenic cascade.Bone. 2016 Dec;93:113-124. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.09.018. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Bone. 2016. PMID: 27664567 Free PMC article.
-
On the Pro-Metastatic Stress Response to Cancer Therapies: Evidence for a Positive Co-Operation between TIMP-1, HIF-1α, and miR-210.Front Pharmacol. 2012 Jul 12;3:134. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00134. eCollection 2012. Front Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22807917 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the tumor vasculature to enhance T cell activity.Curr Opin Immunol. 2015 Apr;33:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25665467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin-angiotensin inhibitors reprogram tumor immune microenvironment: A comprehensive view of the influences on anti-tumor immunity.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 26;9(84):35500-35511. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26174. eCollection 2018 Oct 26. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30464806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11181773', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11181773/'}]}
- Hockel M, Vaupel P (2001) Tumor hypoxia: definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:266–276 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1820761', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1820761/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17043737', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17043737/'}]}
- Padhani AR, Krohn KA, Lewis JS et al (2007) Imaging oxygenation of human tumours. Eur Radiol 17:861–872 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10919633', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10919633/'}]}
- Baish JW, Jain RK (2000) Fractals and cancer. Cancer Res 60:3683–3688 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC549205', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC549205/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '15701176', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15701176/'}]}
- Grizzi F, Russo C, Colombo P et al (2005) Quantitative evaluation and modeling of two-dimensional neovascular network complexity: the surface fractal dimension. BMC Cancer 5:14 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '13130303', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13130303/'}]}
- Semenza GL (2003) Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:721–732 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
