Biochemical analysis of a beta-D-xylosidase and a bifunctional xylanase-ferulic acid esterase from a xylanolytic gene cluster in Prevotella ruminicola 23
- PMID: 19304844
- PMCID: PMC2687155
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01628-08
Biochemical analysis of a beta-D-xylosidase and a bifunctional xylanase-ferulic acid esterase from a xylanolytic gene cluster in Prevotella ruminicola 23
Abstract
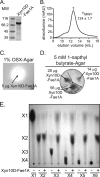
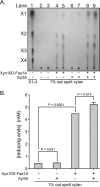
Prevotella ruminicola 23 is an obligate anaerobic bacterium in the phylum Bacteroidetes that contributes to hemicellulose utilization within the bovine rumen. To gain insight into the cellular machinery that this organism elaborates to degrade the hemicellulosic polymer xylan, we identified and cloned a gene predicted to encode a bifunctional xylanase-ferulic acid esterase (xyn10D-fae1A) and expressed the recombinant protein in Escherichia coli. Biochemical analysis of purified Xyn10D-Fae1A revealed that this protein possesses both endo-beta-1,4-xylanase and ferulic acid esterase activities. A putative glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 3 beta-D-glucosidase gene, with a novel PA14-like insertion sequence, was identified two genes downstream of xyn10D-fae1A. Biochemical analyses of the purified recombinant protein revealed that the putative beta-D-glucosidase has activity for pNP-beta-D-xylopyranoside, pNP-alpha-L-arabinofuranoside, and xylo-oligosaccharides; thus, the gene was designated xyl3A. When incubated in combination with Xyn10D-Fae1A, Xyl3A improved the release of xylose monomers from a hemicellulosic xylan substrate, suggesting that these two enzymes function synergistically to depolymerize xylan. Directed mutagenesis studies of Xyn10D-Fae1A mapped the catalytic sites for the two enzymatic functionalities to distinct regions within the polypeptide sequence. When a mutation was introduced into the putative catalytic site for the xylanase domain (E280S), the ferulic acid esterase activity increased threefold, which suggests that the two catalytic domains for Xyn10D-Fae1A are functionally coupled. Directed mutagenesis of conserved residues for Xyl3A resulted in attenuation of activity, which supports the assignment of Xyl3A as a GH family 3 beta-D-xylosidase.
Figures
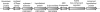
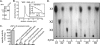
Similar articles
-
Biochemical characterization and relative expression levels of multiple carbohydrate esterases of the xylanolytic rumen bacterium Prevotella ruminicola 23 grown on an ester-enriched substrate.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Aug 15;77(16):5671-81. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05321-11. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21742923 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-xylosidase activity of a GH3 glucosidase/xylosidase from yak rumen metagenome promotes the enzymatic degradation of hemicellulosic xylans.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2012 Feb;54(2):79-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2011.03175.x. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22085266
-
A modular cinnamoyl ester hydrolase from the anaerobic fungus Piromyces equi acts synergistically with xylanase and is part of a multiprotein cellulose-binding cellulase-hemicellulase complex.Biochem J. 1999 Oct 1;343 Pt 1(Pt 1):215-24. Biochem J. 1999. PMID: 10493932 Free PMC article.
-
Functional diversity of four glycoside hydrolase family 3 enzymes from the rumen bacterium Prevotella bryantii B14.J Bacteriol. 2010 May;192(9):2335-45. doi: 10.1128/JB.01654-09. Epub 2010 Feb 26. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20190048 Free PMC article.
-
A mini review of xylanolytic enzymes with regards to their synergistic interactions during hetero-xylan degradation.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Nov 14;35(12):187. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2765-z. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31728656 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional studies on tandem carbohydrate-binding modules of a multimodular enzyme possessing two catalytic domains.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Jul 24;90(7):e0088824. doi: 10.1128/aem.00888-24. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38940565 Free PMC article.
-
Three feruloyl esterases in Cellulosilyticum ruminicola H1 act synergistically to hydrolyze esterified polysaccharides.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Sep;77(17):6141-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00657-11. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21764976 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of roughage on rumen microbiota composition in the efficient feed converter and sturdy Indian Jaffrabadi buffalo (Bubalus bubalis).BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 29;16:1116. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2340-4. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26714477 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic diversity and environment-specific distributions of glycosyl hydrolase family 10 xylanases in geographically distant soils.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043480. Epub 2012 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22912883 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing the economic value of lignocellulosic stillage through medium-chain fatty acid production.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018 Jul 19;11:200. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1193-x. eCollection 2018. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2018. PMID: 30034526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aurilia, V., J. C. Martin, S. I. McCrae, K. P. Scott, M. T. Rincon, and H. J. Flint. 2000. Three multidomain esterases from the cellulolytic rumen anaerobe Ruminococcus flavefaciens 17 that carry divergent dockerin sequences. Microbiology 1461391-1397. - PubMed
-
- Avgustin, G., H. J. Flint, and T. R. Whitehead. 1992. Distribution of xylanase genes and enzymes among strains of Prevotella (Bacteroides) ruminicola from the rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 78137-143. - PubMed
-
- Bergman, E. N. 1990. Energy contributions of volatile fatty acids from the gastrointestinal tract in various species. Physiol. Rev. 70567-590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

