Interferon-gamma coordinates CCL3-mediated neutrophil recruitment in vivo
- PMID: 19298652
- PMCID: PMC2662797
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-10-14
Interferon-gamma coordinates CCL3-mediated neutrophil recruitment in vivo
Abstract
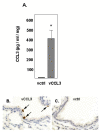
Background: We have shown previously that acute infection with the respiratory pathogen, pneumonia virus of mice (PVM), results in local production of the proinflammatory chemokine, CCL3, and that neutrophil recruitment in response to PVM infection is reduced dramatically in CCL3 -/- mice.
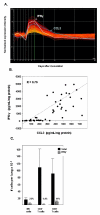
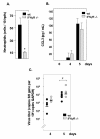
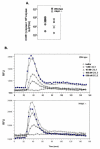
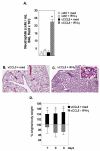
Results: In this work, we demonstrate that CCL3-mediated neutrophil recruitment is coordinated by interferon-gamma (IFNgamma). Neutrophil recruitment in response to PVM infection was diminished five-fold in IFNgamma receptor gene-deleted mice, although neutrophils from IFNgammaR -/- mice expressed transcripts for the CCL3 receptor, CCR1 and responded functionally to CCL3 ex vivo. Similarly, in the absence of PVM infection, CCL3 overexpression alone could not elicit neutrophil recruitment in the absence of IFNgamma. Interestingly, although supplemental IFNgamma restored neutrophil recruitment and resulted in a sustained weight loss among CCL3-overexpressing IFNgamma -/- mice, CCL3-mediated neutrophil recruitment alone did not result in the pulmonary edema or respiratory failure characteristic of severe viral infection, suggesting that CCL3 and IFN-gamma together are sufficient to promote neutrophil recruitment but not pathologic activation.
Conclusion: Our findings reveal a heretofore unrecognized hierarchical interaction between the IFNgamma and CCL3, which demonstrate that IFNgamma is crucial for CCL3-mediated neutrophil recruitment in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sustained inflammation and differential expression of interferons type I and III in PVM-infected interferon-gamma (IFNγ) gene-deleted mice.Virology. 2014 Nov;468-470:140-149. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.07.039. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Virology. 2014. PMID: 25173090 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory responses to pneumovirus infection in IFN-alpha beta R gene-deleted mice.J Immunol. 2005 Oct 1;175(7):4735-44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.7.4735. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16177121
-
Lactobacillus priming of the respiratory tract: Heterologous immunity and protection against lethal pneumovirus infection.Antiviral Res. 2013 Mar;97(3):270-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.12.022. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23274789 Free PMC article.
-
The Pneumonia Virus of Mice (PVM) model of acute respiratory infection.Viruses. 2012 Dec;4(12):3494-510. doi: 10.3390/v4123494. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23342367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pneumonia virus of mice: severe respiratory infection in a natural host.Immunol Lett. 2008 Jun 15;118(1):6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.03.013. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Immunol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18471897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IFN-gamma regulates the requirement for IL-17 in proteoglycan-induced arthritis.J Immunol. 2010 Feb 1;184(3):1552-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902907. Epub 2009 Dec 18. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20028652 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-Dependent Immunity During Pulmonary Infections and Inflammations.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 19;12:689866. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.689866. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34737734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophils contribute to excess serum BAFF levels and promote CD4+ T cell and B cell responses in lupus-prone mice.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 10;9(7):e102284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102284. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25010693 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased leukocyte accumulation and delayed Bordetella pertussis clearance in IL-6-/- mice.J Immunol. 2011 Apr 15;186(8):4895-904. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000594. Epub 2011 Mar 11. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21398615 Free PMC article.
-
Exploitation of Synthetic mRNA To Drive Immune Effector Cell Recruitment and Functional Reprogramming In Vivo.J Immunol. 2019 Jan 15;202(2):608-617. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800924. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30541883 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

