Regulation of antiarrhythmic drug propafenone effects on the c-type Kv1.4 potassium channel by PHo and K+
- PMID: 19270818
- PMCID: PMC2650976
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.1.84
Regulation of antiarrhythmic drug propafenone effects on the c-type Kv1.4 potassium channel by PHo and K+
Abstract
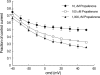
The effects of the antiarrhythmic drug propafenone at c-type kv1.4 channels in Xenopus laevis oocytes were studied with the two-electrode voltage-clamp technique. Defolliculated oocytes (stage V-VI) were injected with transcribed cRNAs of ferret Kv1.4 Delta N channels. During recording, oocytes were continuously perfused with control solution or propafenone. Propafenone decreased the currents during voltage steps. The block was voltage-, use-, and concentration- dependent manners. The block was increased with positive going potentials. The voltage dependence of block could be fitted with the sum of monoexponential and a linear function. Propafenone accelerated the inactivate of current during the voltage step. The concentration of half-maximal block (IC(50)) was 121 microM/L. With high, normal, and low extracellular potassium concentrations, the changes of IC(50) value had no significant statistical differences. The block of propafenone was PH- dependent in high-, normal- and low- extracellular potassium concentrations. Acidification of the extracellular solution to PH 6.0 increased the IC(50) values to 463 microM/L, alkalization to PH 8.0 reduced it to 58 microM/L. The results suggest that propafenone blocks the Kv1.4 Delta N channel in the open state and give some hints for an intracellular site of action.
Keywords: Anti-arrhythmic drug; Ion Channels, Voltage-Gated; Membrane Currents; Potassium Channels; Voltage Clamp.
Figures
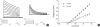


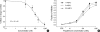

Similar articles
-
Blocking effects of the antiarrhythmic drug propafenone on the HERG potassium channel.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001 Apr;363(4):472-80. doi: 10.1007/s002100000392. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11330342
-
Effect of propafenone on Kv1.4 inactivation.J Physiol Biochem. 2006 Dec;62(4):263-70. doi: 10.1007/BF03165755. J Physiol Biochem. 2006. PMID: 17615952
-
Effect of amiodarone on Kv1.4 channel C-type inactivation: comparison of its effects with those induced by propafenone and verapamil.Pharmazie. 2008 Jun;63(6):475-9. Pharmazie. 2008. PMID: 18604993
-
Molecular site of action of the antiarrhythmic drug propafenone at the voltage-operated potassium channel Kv2.1.Mol Pharmacol. 2003 Mar;63(3):547-56. doi: 10.1124/mol.63.3.547. Mol Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12606761
-
Theoretical possibilities for the development of novel antiarrhythmic drugs.Curr Med Chem. 2004 Jan;11(1):1-11. doi: 10.2174/0929867043456296. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 14754422 Review.
References
-
- Ledda F, Mantelli L, Manzini S, Amerini S, Mugelli A. Electrophysiological and antiarrhythmic properties of propafenon in isolated cardiac preparations. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1981;3:1162–1173. - PubMed
-
- Satoh H, Hashimoto K. Effect of propafenone on the membrane currents of rabbit sino-atrial node cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984;99:185–191. - PubMed
-
- Duan D, Fermini B, Nattel S. Potassium channel blocking properties of propafenone in rabbit atrial myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;264:1113–1123. - PubMed
-
- Hoppe UC, Beuckelmann DJ. Modulation of the hyperpolarization-activated inward current (If) by antiarrhythmic agents in isolated human atrial myocytes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998;358:635–640. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

