Elevated cell invasion is induced by hypoxia in a human pituitary adenoma cell line
- PMID: 19262092
- PMCID: PMC2633679
Elevated cell invasion is induced by hypoxia in a human pituitary adenoma cell line
Abstract
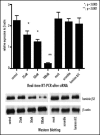
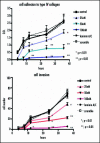
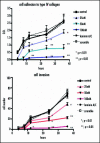
Pituitary adenoma tissues are hypovascular, and have a lower partial oxygen pressure compared with neighboring normal organs. In this study, we investigated whether hypoxia influences the cell invasiveness of the human pituitary adenoma cell line, HP-75. HP-75 cells were exposed to hypoxic (1-10% oxygen) or normoxic (21% oxygen) conditions for 24 hours. Gelatin and reverse zymogram assays were used to determine the enzyme activities of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP). Cell adhesion and Matrigel cell invasion were examined with a Boiden chamber. Finally, the mRNA gene expression profiles of cells exposed to hypoxia or normoxia were examined by cDNA microarray and confirmed with real-time RT-PCR and flow cytometry. The gelatin and reverse zymograms revealed that the activities of MMP and TIMP were not significantly altered by hypoxia. Matrigel cell invasion and cell adhesion to Matrigel or collagen type IV were increased by hypoxia (3.8- and 4.8-fold, respectively). The cDNA microarray analysis revealed that laminin beta2 chain mRNA was specifically up-regulated under hypoxic conditions (4.96-fold). Finally, real-time RT-PCR and flow cytometry verified the elevated expression of laminin beta2 chain at the mRNA and protein levels under hypoxic conditions. RNA interference with siRNA targeting laminin beta2 inhibited Matrigel invasion and adhesion to collagen type IV in a dose-dependent manner. Collectively, these results suggested that hypoxia (1% oxygen) enhanced the cell invasion properties of a pituitary adenoma cell line in association with elevated expression of laminin beta2 and enhanced binding to collagen type IV.
Figures
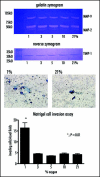
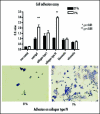
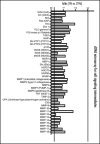
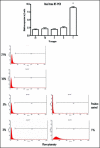
Similar articles
-
Expression of laminin beta2: a novel marker of hypoxia in pituitary adenomas.Endocr Pathol. 2006 Fall;17(3):251-61. doi: 10.1385/ep:17:3:251. Endocr Pathol. 2006. PMID: 17308362
-
The CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 suppresses hypoxia-mediated growth hormone production in GH3 rat pituitary adenoma cells.J Neurooncol. 2010 Oct;100(1):51-64. doi: 10.1007/s11060-010-0152-6. Epub 2010 Mar 23. J Neurooncol. 2010. PMID: 20309720
-
Enhancement of pituitary adenoma cell invasion and adhesion is mediated by discoidin domain receptor-1.J Neurooncol. 2007 Mar;82(1):29-40. doi: 10.1007/s11060-006-9246-6. Epub 2006 Sep 26. J Neurooncol. 2007. PMID: 17001518
-
Effect of Hypoxia on DDR1 Expression in Pituitary Adenomas.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Aug 19;21:2433-8. doi: 10.12659/MSM.894205. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26286316 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of aggressive pituitary adenomas.J Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Aug 30;49(2):R69-78. doi: 10.1530/JME-12-0113. Print 2012 Oct. J Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22822048 Review.
Cited by
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation inhibits tumor metastasis by antagonizing Smad3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Dec;9(12):3221-32. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0570. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 21159608 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia promotes proliferation of pituitary adenomas by HIF-1α/ALKBH5 signaling in vitro.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 May 1;13(5):1030-1034. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32509075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lolkema MP, Gervais ML, Snijckers CM, Hill RP, Giles RH, Voest EE, Ohh M. Tumor suppression by the von Hippel-Lindau protein requires phosphorylation of the acidic domain. J Biol Chem. 2005 - PubMed
-
- Heinl-Green A, Radke PW, Munkonge FM, Frass O, Zhu J, Vincent K, Geddes DM, Alton EW. The efficacy of a ‘master switch gene’ HIF-1{alpha} in a porcine model of chronic myocardial ischaemia. Eur Heart J. 2005 - PubMed
-
- Kondo Y, Hamada J, Kobayashi C, Nakamura R, Suzuki Y, Kimata R, Nishimura T, Kitagawa T, Kunimoto M, Imura N, Hara S. Over expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in renal and bladder cancer cells increases tumorigenic potency. J Urol. 2005;173:1762–1766. - PubMed
-
- Hamrick SE, McQuillen PS, Jiang X, Mu D, Madan A, Ferriero DM. A role for hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in desferoxamine neuroprotection. Neurosci Lett. 2005;379:96–100. - PubMed
-
- Han XJ, Chae JK, Lee MJ, You KR, Lee BH, Kim DG. Involvement of GADD153 and cardiac ankyrin repeat protein in hypoxia-induced apoptosis of H9c2 cells. J Biol Chem. 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
