Scaling pharmacodynamics from in vitro and preclinical animal studies to humans
- PMID: 19252333
- PMCID: PMC3727168
- DOI: 10.2133/dmpk.24.16
Scaling pharmacodynamics from in vitro and preclinical animal studies to humans
Abstract
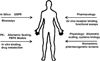
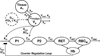
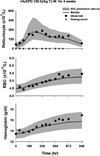
An important feature of mechanism-based pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) models is the identification of drug- and system-specific factors that determine the intensity and time-course of pharmacological effects. This provides an opportunity to integrate information obtained from in vitro bioassays and preclinical pharmacological studies in animals to anticipate the clinical and adverse responses to drugs in humans. The fact that contemporary PK/PD modeling continues to evolve and seeks to emulate systems level properties should provide enhanced capabilities to scale-up pharmacodynamic data. Critical steps in drug discovery and development, such as lead compound and first in human dose selection, may become more efficient with the implementation and further refinement of translational PK/PD modeling. In this review, we highlight fundamental principles in pharmacodynamics and the basic expectations for in vitro bioassays and traditional allometric scaling in PK/PD modeling. Discussion of PK/PD modeling efforts for recombinant human erythropoietin is also included as a case study showing the potential for advanced systems analysis to facilitate extrapolations and improve understanding of inter-species differences in drug responses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Incorporating receptor theory in mechanism-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) modeling.Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2009;24(1):3-15. doi: 10.2133/dmpk.24.3. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2009. PMID: 19252332 Review.
-
Preclinical pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling and simulation in the pharmaceutical industry: an IQ consortium survey examining the current landscape.AAPS J. 2015 Mar;17(2):462-73. doi: 10.1208/s12248-014-9716-2. Epub 2015 Jan 29. AAPS J. 2015. PMID: 25630504 Free PMC article.
-
Translational PK/PD modeling for cardiovascular safety assessment of drug candidates: Methods and examples in drug development.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2014 Jul-Aug;70(1):73-85. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 28. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24879942
-
Development of translational pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Jun;83(6):909-12. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2008.52. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18388873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic modelling for starting dose selection in first-in-human trials of high-risk biologics.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;67(2):153-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03297.x. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19076987 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Target-Mediated Drug Disposition Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Model-Informed Dose Selection for the First-in-Human Study of AVB-S6-500.Clin Transl Sci. 2020 Jan;13(1):204-211. doi: 10.1111/cts.12706. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Clin Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 31599479 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Implementation of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic strategies in early research phases of drug discovery and development at Novartis Institute of Biomedical Research.Front Pharmacol. 2014 Jul 28;5:174. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00174. eCollection 2014. Front Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25120485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of a Therapeutic Dose for Buagafuran, a Potent Anxiolytic Agent by Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modeling Starting from Pharmacokinetics in Rats and Human.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 10;8:683. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00683. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29066968 Free PMC article.
-
The mastermind approach to CNS drug therapy: translational prediction of human brain distribution, target site kinetics, and therapeutic effects.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2013 Feb 22;10(1):12. doi: 10.1186/2045-8118-10-12. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2013. PMID: 23432852 Free PMC article.
-
Scaling Pharmacodynamics from Rats to Humans to Support Erythropoietin and Romiplostim Combination Therapy to Treat Erythropoietin-Resistant Anemia.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 19;15(2):344. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020344. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nestorov I. Whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic models. Expert Opin. Drug. Metab. Toxicol. 2007;3:235–249. - PubMed
-
- Mager DE. Quantitative structure-pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationships. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006;58:1326–1356. - PubMed
-
- Beliveau M, Lipscomb J, Tardif R, Krishnan K. Quantitative structure-property relationships for interspecies extrapolation of the inhalation pharmacokinetics of organic chemicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005;18:475–485. - PubMed
-
- Parrott N, Paquereau N, Coassolo P, Lave T. An evaluation of the utility of physiologically based models of pharmacokinetics in early drug discovery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005;94:2327–2343. - PubMed
-
- Danhof M, de Jongh J, De Lange ECM, Della Pasqua O, Ploeger BA, Voskuyl RA. Mechanism-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling: Biophase distribution, receptor theory, and dynamical systems analysis. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007;47:21.21–21.44. - PubMed
