Down-regulation of the inhibitor of growth family member 4 (ING4) in different forms of pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 19250543
- PMCID: PMC2662808
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-10-14
Down-regulation of the inhibitor of growth family member 4 (ING4) in different forms of pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Recent evidence has underscored the role of hypoxia and angiogenesis in the pathogenesis of idiopathic fibrotic lung disease. Inhibitor of growth family member 4 (ING4) has recently attracted much attention as a tumor suppressor gene, due to its ability to inhibit cancer cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis. The aim of our study was to investigate the role of ING4 in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis both in the bleomycin (BLM)-model and in two different types of human pulmonary fibrosis, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP).
Methods: Experimental model of pulmonary fibrosis was induced by a single tail vein injection of bleomycin in 6- to 8-wk-old C57BL/6mice. Tissue microarrays coupled with qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry were applied in whole lung samples and paraffin-embedded tissue sections of 30 patients with IPF, 20 with COP and 20 control subjects.
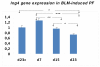
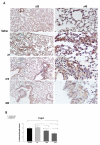
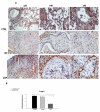
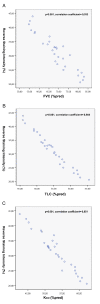
Results: A gradual decline of ING4 expression in both mRNA and protein levels was reported in the BLM-model. ING4 was also found down-regulated in IPF patients compared to COP and control subjects. Immunolocalization analyses revealed increased expression in areas of normal epithelium and in alveolar epithelium surrounding Masson bodies, in COP lung, whereas showed no expression within areas of active fibrosis within IPF and COP lung. In addition, ING4 expression levels were negatively correlated with pulmonary function parameters in IPF patients.
Conclusion: Our data suggest a potential role for ING4 in lung fibrogenesis. ING4 down-regulation may facilitate aberrant vascular remodelling and fibroblast proliferation and migration leading to progressive disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1a-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-inhibitory growth factor (ING)-4- axis in sarcoidosis patients.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Nov 26;5:654. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-654. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 23181555 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) in patients with different forms of lung fibrosis.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:654354. doi: 10.1155/2013/654354. Epub 2013 Jun 9. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23841084 Free PMC article.
-
Role of lung apolipoprotein A-I in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect on experimental lung injury and fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010 Sep 1;182(5):633-42. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200905-0659OC. Epub 2010 May 12. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20463180
-
MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Transl Res. 2011 Apr;157(4):191-9. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.01.012. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21420029 Review.
-
Sphingolipids in pulmonary fibrosis.Adv Biol Regul. 2015 Jan;57:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.09.008. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Adv Biol Regul. 2015. PMID: 25446881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of the tumor suppressor gene ING4 on the proliferation of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2012 Sep;4(3):438-442. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.744. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22970041 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ING4 (inhibitor of growth 4) as a modulator of docetaxel sensitivity in human lung adenocarcinoma.Mol Med. 2012 Jul 18;18(1):874-86. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00230. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22460125 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1a-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-inhibitory growth factor (ING)-4- axis in sarcoidosis patients.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Nov 26;5:654. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-654. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 23181555 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of ING4 is associated with initiation and progression of lung cancer.Histopathology. 2010 Aug;57(2):271-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03623.x. Histopathology. 2010. PMID: 20716169 Free PMC article.
-
The essential role of tumor suppressor gene ING4 in various human cancers and non-neoplastic disorders.Biosci Rep. 2019 Jan 30;39(1):BSR20180773. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180773. Print 2019 Jan 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30643005 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(2):277–304. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161(2 Pt 1):646–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

