Microtubule nucleation at the cis-side of the Golgi apparatus requires AKAP450 and GM130
- PMID: 19242490
- PMCID: PMC2683699
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.47
Microtubule nucleation at the cis-side of the Golgi apparatus requires AKAP450 and GM130
Abstract
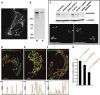
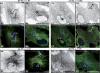
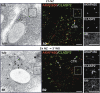
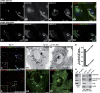
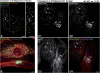
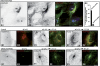
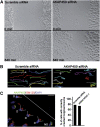
We report that microtubule (MT) nucleation at the Golgi apparatus requires AKAP450, a centrosomal gamma-TuRC-interacting protein that also forms a distinct network associated with the Golgi. Depletion of AKAP450 abolished MT nucleation at the Golgi, whereas depletion of the cis-Golgi protein GM130 led to the disorganisation of AKAP450 network and impairment of MT nucleation. Brefeldin-A treatment induced relocalisation of AKAP450 to ER exit sites and concomitant redistribution of MT nucleation capacity to the ER. AKAP450 specifically binds the cis-side of the Golgi in an MT-independent, GM130-dependent manner. Short AKAP450-dependent growing MTs are covered by CLASP2. Like for centrosome, dynein/dynactin complexes are necessary to anchor MTs growing from the Golgi. We further show that Golgi-associated AKAP450 has a role in cell migration rather than in cell polarisation of the centrosome-Golgi apparatus. We propose that the recruitment of AKAP450 on the Golgi membranes through GM130 allows centrosome-associated nucleating activity to extend to the Golgi, to control the assembly of subsets of MTs ensuring specific functions within the Golgi or for transporting specific cargos to the cell periphery.
Figures



Comment in
-
A new function for an old organelle: microtubule nucleation at the Golgi apparatus.EMBO J. 2009 Apr 22;28(8):995-6. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.85. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19384347 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Disconnecting the Golgi ribbon from the centrosome prevents directional cell migration and ciliogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2011 May 30;193(5):917-33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201011014. Epub 2011 May 23. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21606206 Free PMC article.
-
Function of Golgi-centrosome proximity in RPE-1 cells.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 15;14(4):e0215215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215215. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30986258 Free PMC article.
-
The dual role of the centrosome in organizing the microtubule network in interphase.EMBO Rep. 2018 Nov;19(11):e45942. doi: 10.15252/embr.201845942. Epub 2018 Sep 17. EMBO Rep. 2018. PMID: 30224411 Free PMC article.
-
The centrosome-Golgi apparatus nexus.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Sep 5;369(1650):20130462. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0462. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25047616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABARAP activates ULK1 and traffics from the centrosome dependent on Golgi partners WAC and GOLGA2/GM130.Autophagy. 2016 May 3;12(5):892-3. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1159368. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 26986052 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
γ-Tubulin Complexes and Fibrillar Arrays: Two Conserved High Molecular Forms with Many Cellular Functions.Cells. 2021 Apr 1;10(4):776. doi: 10.3390/cells10040776. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33915825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Centrosomal AKAP350 and CIP4 act in concert to define the polarized localization of the centrosome and Golgi in migratory cells.J Cell Sci. 2015 Sep 1;128(17):3277-89. doi: 10.1242/jcs.170878. Epub 2015 Jul 24. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26208639 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule nucleation and organization in dendrites.Cell Cycle. 2016 Jul 2;15(13):1685-92. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1172158. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27097122 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved motif of CDK5RAP2 mediates its localization to centrosomes and the Golgi complex.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):22658-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.105965. Epub 2010 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20466722 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Golgi ribbon.Traffic. 2010 Nov;11(11):1391-400. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01114.x. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 21040294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartolini F, Gundersen GG (2006) Generation of noncentrosomal microtubule arrays. J Cell Sci 119: 4155–4163 - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R (2002) A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296: 550–553 - PubMed
-
- Burakov A, Kovalenko O, Semenova I, Zhapparova O, Nadezhdina E, Rodionov V (2008) Cytoplasmic dynein is involved in the retention of microtubules at the centrosome in interphase cells. Traffic 9: 472–480 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

