Signals for the execution of Th2 effector function
- PMID: 19237299
- PMCID: PMC2955979
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.12.023
Signals for the execution of Th2 effector function
Abstract
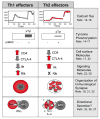
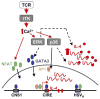
Appropriate control of infection depends on the generation of lymphocytes armed with a particular array of cytokine and chemokine effector molecules. The differentiation of naïve T cells into functionally distinct effector subsets is regulated by signals from the T cell receptor (TCR) and cytokine receptors. Using gene knock-out approaches, the initiation of discrete effector programs appears differentially sensitive to the loss of individual TCR signaling components; likely due to differences in the transcription factors needed to activate individual cytokine genes. Less well understood however, are the signal requirements for the execution of effector function. With a focus on Th2 cells and the kinase ITK, we review recent observations that point to differences between the signals needed for the initiation and implementation of cytokine programs in CD4+ T cells. Indeed, Th2 effector cells signal differently from both their naïve counterparts and from Th1 effectors suggesting they may transduce activation signals differently or may be selectively receptive to different activation signals. Potential regulation points for effector function lie at the level of transcription and translation of cytokine genes. We also discuss how provision of these execution signals may be spatially segregated in vivo occurring at tissue sites of inflammation and subject to modulation by the pathogen itself.
Figures
Similar articles
-
'All things considered': transcriptional regulation of T helper type 2 cell differentiation from precursor to effector activation.Immunology. 2013 Sep;140(1):31-8. doi: 10.1111/imm.12121. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23668241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naive and effector CD4 T cells differ in their requirements for T cell receptor versus costimulatory signals.J Immunol. 1996 Oct 15;157(8):3280-9. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8871622
-
Cutting edge: Itk-dependent signals required for CD4+ T cells to exert, but not gain, Th2 effector function.J Immunol. 2006 Apr 1;176(7):3895-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.7.3895. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16547221
-
Strength of TCR signal determines the costimulatory requirements for Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cell differentiation.J Immunol. 1997 Dec 15;159(12):5956-63. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9550393
-
In Vivo CD4+ T Cell Differentiation and Function: Revisiting the Th1/Th2 Paradigm.Annu Rev Immunol. 2020 Apr 26;38:705-725. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-103019-085803. Annu Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32340571 Review.
Cited by
-
A conserved motif in the ITK PH-domain is required for phosphoinositide binding and TCR signaling but dispensable for adaptor protein interactions.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045158. Epub 2012 Sep 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028816 Free PMC article.
-
CD4+ T helper 2 cells--microbial triggers, differentiation requirements and effector functions.Immunology. 2011 Dec;134(4):368-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03497.x. Immunology. 2011. PMID: 22043920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of immune responsiveness in vivo by disrupting an early T-cell signaling event using a cell-permeable peptide.PLoS One. 2013 May 7;8(5):e63645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063645. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23667652 Free PMC article.
-
Critical requirement for the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein in Th2 effector function.Blood. 2010 Apr 29;115(17):3498-507. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-235754. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20032499 Free PMC article.
-
Sickness behavior induced by endotoxin can be mitigated by the dietary soluble fiber, pectin, through up-regulation of IL-4 and Th2 polarization.Brain Behav Immun. 2010 May;24(4):631-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.01.015. Epub 2010 Feb 6. Brain Behav Immun. 2010. PMID: 20138982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Au-Yeung BB, Katzman SD, Fowell DJ. Cutting edge: Itk-dependent signals required for CD4+ T cells to exert, but not gain, Th2 effector function. J Immunol. 2006;176:3895–3899. - PubMed
-
- Darrah PA, Patel DT, De Luca PM, Lindsay RW, Davey DF, Flynn BJ, Hoff ST, Andersen P, Reed SG, Morris SL, Roederer M, Seder RA. Multifunctional TH1 cells define a correlate of vaccine-mediated protection against Leishmania major. Nat Med. 2007;13:843–850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

