Expression analysis of the CLCA gene family in mouse and human with emphasis on the nervous system
- PMID: 19210762
- PMCID: PMC2653474
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-10
Expression analysis of the CLCA gene family in mouse and human with emphasis on the nervous system
Abstract
Background: Members of the calcium-activated chloride channel (CLCA) gene family have been suggested to possess a variety of functions including cell adhesion and tumor suppression. Expression of CLCA family members has mostly been analyzed in non-neural tissues. Here we describe the expression of mouse and human CLCA genes in the nervous system.
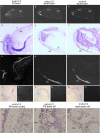
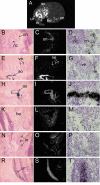
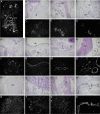
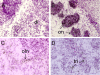
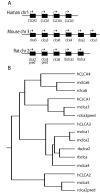
Results: We show that from the six mouse CLCA family members only Clca1, Clca2 and Clca4 mRNAs are expressed in the adult brain, predominantly in olfactory ensheathing cells. During mouse nervous system development Clca1/2 is more widely expressed, particularly in cranial nerves, the diencephalon and in the cerebral cortex. While human CLCA2 and CLCA4 genes are widely expressed in brain, and at particularly high levels in the optic nerve, human CLCA3, the closest homologue of mouse Clca1, Clca2 and Clca4, is not expressed in the brain. Furthermore, we characterize the expression pattern of mouse Clca1/2 genes during embryonic development by in situ hybridization.
Conclusion: The data published in this article indicate that within the nervous system mouse Clca1/2 genes are highly expressed in the cells ensheathing cranial nerves. Human CLCA2 and CLCA4 mRNAs are expressed at high level in optic nerve. High level expression of CLCA family members in mouse and human glial cells ensheathing nerves suggests a specific role for CLCA proteins in the development and homeostasis of these cells.
Figures
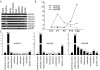
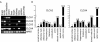
Similar articles
-
Clustering of the human CLCA gene family on the short arm of chromosome 1 (1p22-31).Genome. 1999 Oct;42(5):1030-2. doi: 10.1139/g99-006. Genome. 1999. PMID: 10584316
-
Modulation of TMEM16B channel activity by the calcium-activated chloride channel regulator 4 (CLCA4) in human cells.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jul;300(7):107432. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107432. Epub 2024 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38825009 Free PMC article.
-
The Family of Chloride Channel Regulator, Calcium-activated Proteins in the Feline Respiratory Tract: A Comparative Perspective on Airway Diseases in Man and Animal Models.J Comp Pathol. 2020 Jan;174:39-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2019.10.193. Epub 2019 Nov 29. J Comp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31955802
-
Structure and function of CLCA proteins.Physiol Rev. 2005 Jul;85(3):1061-92. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00016.2004. Physiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15987802 Review.
-
Molecular characteristics and functional diversity of CLCA family members.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000 Nov;27(11):901-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2000.03358.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11071307 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of the CLCA4 Gene in Esophageal Carcinoma and Its Impact on the Biologic Function of Esophageal Carcinoma Cells.J Oncol. 2021 Jun 4;2021:1649344. doi: 10.1155/2021/1649344. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34194494 Free PMC article.
-
Ion transporter NKCC1, modulator of neurogenesis in murine olfactory neurons.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9767-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.640656. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25713142 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of CLCA4 expression is associated with the development and progression of colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Jul;20(1):631-638. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11640. Epub 2020 May 18. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32565987 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-expression analysis of early- and late-maturation-stage rat enamel organ.Eur J Oral Sci. 2011 Dec;119 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):149-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2011.00881.x. Eur J Oral Sci. 2011. PMID: 22243241 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Hub Genes in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma by Integrated Bioinformatics.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 May 27;10:897568. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.897568. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35693937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gruber AD, Pauli BU. Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a truncated, secreted member of the human family of Ca2+-activated Cl- channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1444:418–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

