Nascent peptide-dependent translation arrest leads to Not4p-mediated protein degradation by the proteasome
- PMID: 19204001
- PMCID: PMC2667721
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808840200
Nascent peptide-dependent translation arrest leads to Not4p-mediated protein degradation by the proteasome
Abstract
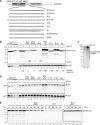
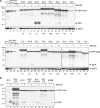
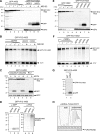
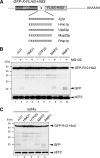
The potentially deleterious effects of aberrant mRNA lacking a termination codon (nonstop mRNA) are ameliorated by translation arrest, proteasome-mediated protein destabilization, and rapid mRNA degradation. Because polylysine synthesis via translation of the poly(A) mRNA tail leads to translation arrest and protein degradation by the proteasome, we examined the effects of other amino acid sequences. Insertion of 12 consecutive basic amino acids between GFP and HIS3 reporter genes, but not a stem-loop structure, resulted in degradation of the truncated green fluorescent protein (GFP) products by the proteasome. Translation arrest products derived from GFP-R12-FLAG-HIS3 or GFP-K12-FLAG-HIS3 mRNA were detected in a not4Delta mutant, and MG132 treatment did not affect the levels of the truncated arrest products. Deletion of other components of the Ccr4-Not complex did not increase the levels of the translation arrest products or reporter mRNAs. A L35A substitution in the Not4p RING finger domain, which disrupted its interaction with the Ubc4/Ubc5 E2 enzyme and its activity as an ubiquitin-protein ligase, also abrogated the degradation of arrest products. These results suggest that Not4p, a component of the Ccr4-Not complex, may act as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase for translation arrest products. The results let us propose that the interaction between basic amino acid residues and the negatively charged exit tunnel of the ribosome leads to translation arrest followed by Not4p-mediated ubiquitination and protein degradation by the proteasome.
Figures
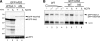
Similar articles
-
Protein quality control systems associated with no-go and nonstop mRNA surveillance in yeast.Genes Cells. 2014 Jan;19(1):1-12. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12106. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Genes Cells. 2014. PMID: 24261871
-
Modulation of Ubc4p/Ubc5p-mediated stress responses by the RING-finger-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase Not4p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2007 May;176(1):181-92. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.060640. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17513889 Free PMC article.
-
Rqc1 and Ltn1 Prevent C-terminal Alanine-Threonine Tail (CAT-tail)-induced Protein Aggregation by Efficient Recruitment of Cdc48 on Stalled 60S Subunits.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 3;291(23):12245-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.722264. Epub 2016 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129255 Free PMC article.
-
Quality control systems for aberrant mRNAs induced by aberrant translation elongation and termination.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun-Jul;1829(6-7):634-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23416749 Review.
-
Influence of nascent polypeptide positive charges on translation dynamics.Biochem J. 2020 Aug 14;477(15):2921-2934. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200303. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32797214 Review.
Cited by
-
The Not4 RING E3 Ligase: A Relevant Player in Cotranslational Quality Control.ISRN Mol Biol. 2013 Jan 21;2013:548359. doi: 10.1155/2013/548359. eCollection 2013. ISRN Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 27335678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Net -1 frameshifting on a noncanonical sequence in a herpes simplex virus drug-resistant mutant is stimulated by nonstop mRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 11;109(37):14852-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206582109. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22927407 Free PMC article.
-
ZNF598 Is a Quality Control Sensor of Collided Ribosomes.Mol Cell. 2018 Nov 1;72(3):469-481.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.037. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30293783 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual mammalian usage of TGA stop codons reveals that sequence conservation need not imply purifying selection.PLoS Biol. 2022 May 12;20(5):e3001588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001588. eCollection 2022 May. PLoS Biol. 2022. PMID: 35550630 Free PMC article.
-
A ubiquitin language communicates ribosomal distress.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 15;154(Pt B):131-137. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2023.03.009. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 36963992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

