Kinetoplastid RNA editing involves a 3' nucleotidyl phosphatase activity
- PMID: 19190092
- PMCID: PMC2665232
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp049
Kinetoplastid RNA editing involves a 3' nucleotidyl phosphatase activity
Abstract
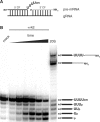
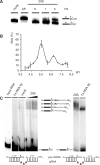
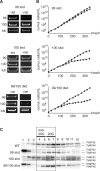
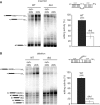
Mitochondrial pre-messenger RNAs (pre-mRNAs) in African trypanosomes require RNA editing in order to mature into functional transcripts. The process involves the addition and/or removal of U nucleotides and is mediated by a high-molecular-mass complex, the editosome. Editosomes catalyze the reaction through an enzyme-driven pathway that includes endo/exoribonuclease, terminal uridylate transferase and RNA ligase activities. Here we show that editing involves an additional reaction step, a 3' nucleotidyl phosphatase activity. The activity is associated with the editing complex and we demonstrate that the editosomal proteins TbMP99 and TbMP100 contribute to the activity. Both polypeptides contain endo-exonuclease-phosphatase domains and we show that gene ablation of either one of the two polypeptides is compensated by the other protein. However, simultaneous knockdown of both genes results in trypanosome cells with reduced 3' nucleotidyl phosphatase and reduced editing activity. The data provide a rationale for the exoUase activity of the editosomal protein TbMP42, which generates nonligatable 3' phosphate termini. Opposing phosphates at the two pre-mRNA cleavage fragments likely function as a roadblock to prevent premature ligation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In Trypanosoma brucei RNA editing, TbMP18 (band VII) is critical for editosome integrity and for both insertional and deletional cleavages.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jan;27(2):777-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01460-06. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17101787 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma brucei RNA editing protein TbMP42 (band VI) is crucial for the endonucleolytic cleavages but not the subsequent steps of U-deletion and U-insertion.RNA. 2008 Jun;14(6):1187-200. doi: 10.1261/rna.899508. Epub 2008 Apr 25. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18441050 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of a functional enzymatic editing complex from Trypanosoma brucei mitochondria.EMBO J. 1997 Jul 1;16(13):4069-81. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.13.4069. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9233816 Free PMC article.
-
Insertional and deletional RNA editing in trypanosome mitochondria.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1997;(36):15-8. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1997. PMID: 9478193 Review.
-
RNA editing: complexity and complications.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Aug;45(3):591-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03028.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12139607 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel member of the RNase D exoribonuclease family functions in mitochondrial guide RNA metabolism in Trypanosoma brucei.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 25;286(12):10329-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.152439. Epub 2011 Jan 20. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21252235 Free PMC article.
-
Editosome accessory factors KREPB9 and KREPB10 in Trypanosoma brucei.Eukaryot Cell. 2012 Jul;11(7):832-43. doi: 10.1128/EC.00046-12. Epub 2012 May 4. Eukaryot Cell. 2012. PMID: 22562468 Free PMC article.
-
Uridine insertion/deletion editing in trypanosomes: a playground for RNA-guided information transfer.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Sep-Oct;2(5):669-85. doi: 10.1002/wrna.82. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21823228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Editosome Protein Function between Life Cycle Stages of Trypanosoma brucei.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 9;290(41):24914-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.669432. Epub 2015 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26304125 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for guide RNA trimming by RNase D ribonuclease in Trypanosoma brucei.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 11;49(1):568-583. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1197. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33332555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madison-Antenucci S, Grams J, Hajduk SL. Editing machines: the complexities of trypanosome RNA editing. Cell. 2002;108:435–438. - PubMed
-
- Carnes J, Stuart K. Working together: the RNA editing machinery in Trypanosoma brucei. In: Göringer HU, editor. RNA Editing. Heidelberg: Springer; 2008. pp. 143–164.
-
- Seiwert SD, Heidmann S, Stuart K. Direct visualization of uridylate deletion in vitro suggests a mechanism for kinetoplastid RNA editing. Cell. 1996;84:831–841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

