Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals
- PMID: 19182780
- PMCID: PMC2754849
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07672
Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals
Abstract
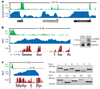
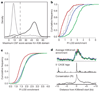
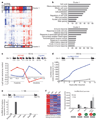
There is growing recognition that mammalian cells produce many thousands of large intergenic transcripts. However, the functional significance of these transcripts has been particularly controversial. Although there are some well-characterized examples, most (>95%) show little evidence of evolutionary conservation and have been suggested to represent transcriptional noise. Here we report a new approach to identifying large non-coding RNAs using chromatin-state maps to discover discrete transcriptional units intervening known protein-coding loci. Our approach identified approximately 1,600 large multi-exonic RNAs across four mouse cell types. In sharp contrast to previous collections, these large intervening non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) show strong purifying selection in their genomic loci, exonic sequences and promoter regions, with greater than 95% showing clear evolutionary conservation. We also developed a functional genomics approach that assigns putative functions to each lincRNA, demonstrating a diverse range of roles for lincRNAs in processes from embryonic stem cell pluripotency to cell proliferation. We obtained independent functional validation for the predictions for over 100 lincRNAs, using cell-based assays. In particular, we demonstrate that specific lincRNAs are transcriptionally regulated by key transcription factors in these processes such as p53, NFkappaB, Sox2, Oct4 (also known as Pou5f1) and Nanog. Together, these results define a unique collection of functional lincRNAs that are highly conserved and implicated in diverse biological processes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Missing lincs in the transcriptome.Nat Biotechnol. 2009 Apr;27(4):346-7. doi: 10.1038/nbt0409-346. Nat Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19352372 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Missing lincs in the transcriptome.Nat Biotechnol. 2009 Apr;27(4):346-7. doi: 10.1038/nbt0409-346. Nat Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19352372 No abstract available.
-
Chromatin environment, transcriptional regulation, and splicing distinguish lincRNAs and mRNAs.Genome Res. 2017 Jan;27(1):27-37. doi: 10.1101/gr.214205.116. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Genome Res. 2017. PMID: 27927715 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors KANADI 1, MYB DOMAIN PROTEIN 44, and PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 4 regulate long intergenic noncoding RNAs expressed in Arabidopsis roots.Plant Physiol. 2023 Oct 26;193(3):1933-1953. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad360. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37345955
-
Long noncoding RNA (lincRNA), a new paradigm in gene expression control.Funct Integr Genomics. 2017 May;17(2-3):135-143. doi: 10.1007/s10142-016-0524-x. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 27681237 Review.
-
The mystery of extreme non-coding conservation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Nov 11;368(1632):20130021. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0021. Print 2013 Dec 19. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24218634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of long noncoding RNAs in livestock adipose tissue deposition - A review.Anim Biosci. 2021 Jul;34(7):1089-1099. doi: 10.5713/ab.21.0006. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Anim Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33902176 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing the interactions of mRNAs, miRNAs and lncRNAs to predict ceRNA networks in bovine cystic follicular granulosa cells.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Oct 13;9:1028867. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1028867. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36311668 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread Inducible Transcription Downstream of Human Genes.Mol Cell. 2015 Aug 6;59(3):449-61. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26190259 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNA: a new frontier in regulatory biology.Natl Sci Rev. 2014 Jun 1;1(2):190-204. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwu008. Natl Sci Rev. 2014. PMID: 25821635 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying recent adaptations in large-scale genomic data.Cell. 2013 Feb 14;152(4):703-13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.035. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23415221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertone P, et al. Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Science. 2004;306:2242–2246. - PubMed
-
- Carninci P, et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science. 2005;309:1559–1563. - PubMed
-
- Kapranov P, et al. Large-scale transcriptional activity in chromosomes 21 and 22. Science. 2002;296:916–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

